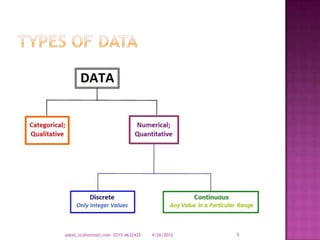
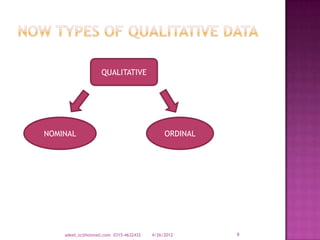
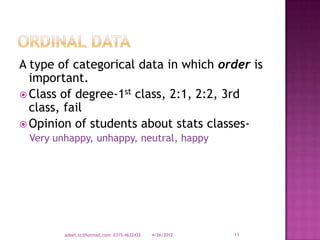
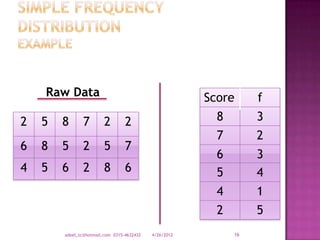
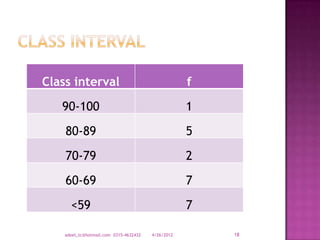
The document provides a comprehensive overview of data types and categories, explaining qualitative and quantitative data, including discrete and continuous data. It describes sources of data, various representations, and how to organize and summarize data through distributions and frequency tables. Additionally, it highlights the importance of class intervals in data analysis.