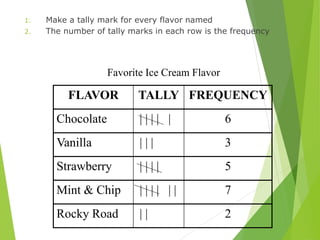
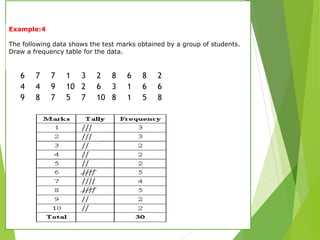
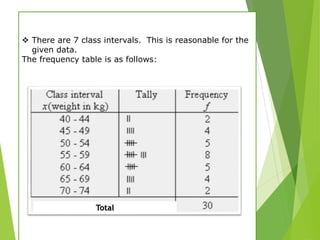
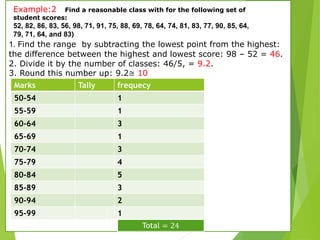
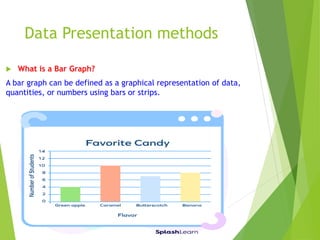
The document outlines various data presentation methods including frequency tables, bar charts, pie charts, histograms, and line plots. It provides examples for constructing frequency tables with and without class intervals, as well as guidelines for creating bar graphs and pie charts. Additionally, it explains how to interpret and analyze data through these visual representations.