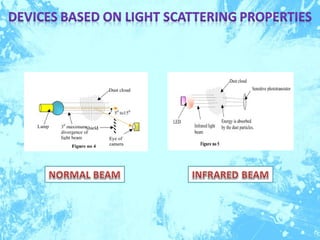
The document discusses various dust suppression systems used in industrial settings including spray systems, foggers, centrifugal dust collectors, and electrostatic precipitators. It provides details on the operation and components of each type of system as well as factors to consider like efficiency, cost, and impact on product quality. References are also included that provide additional information on controlling respirable dust.