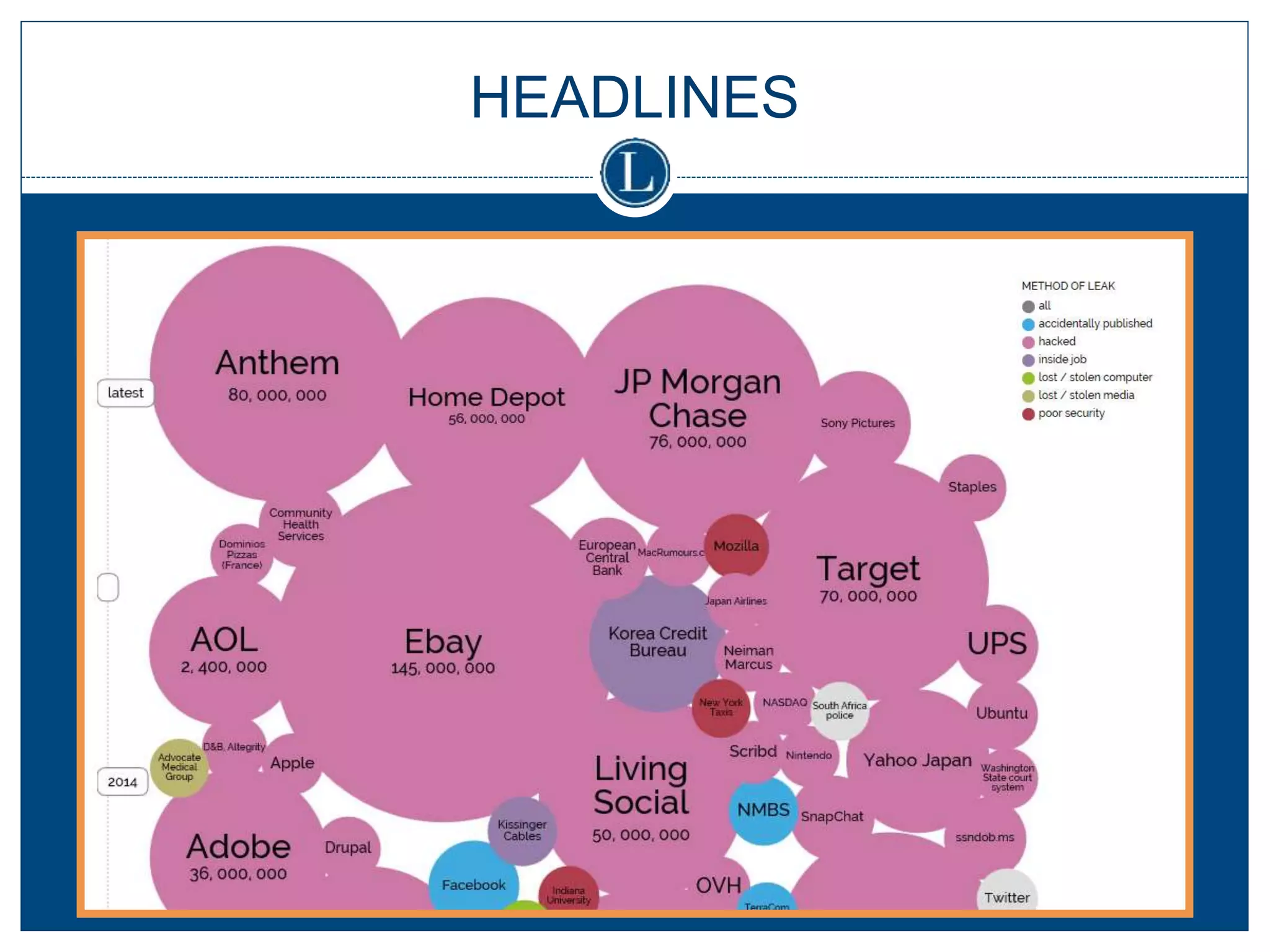
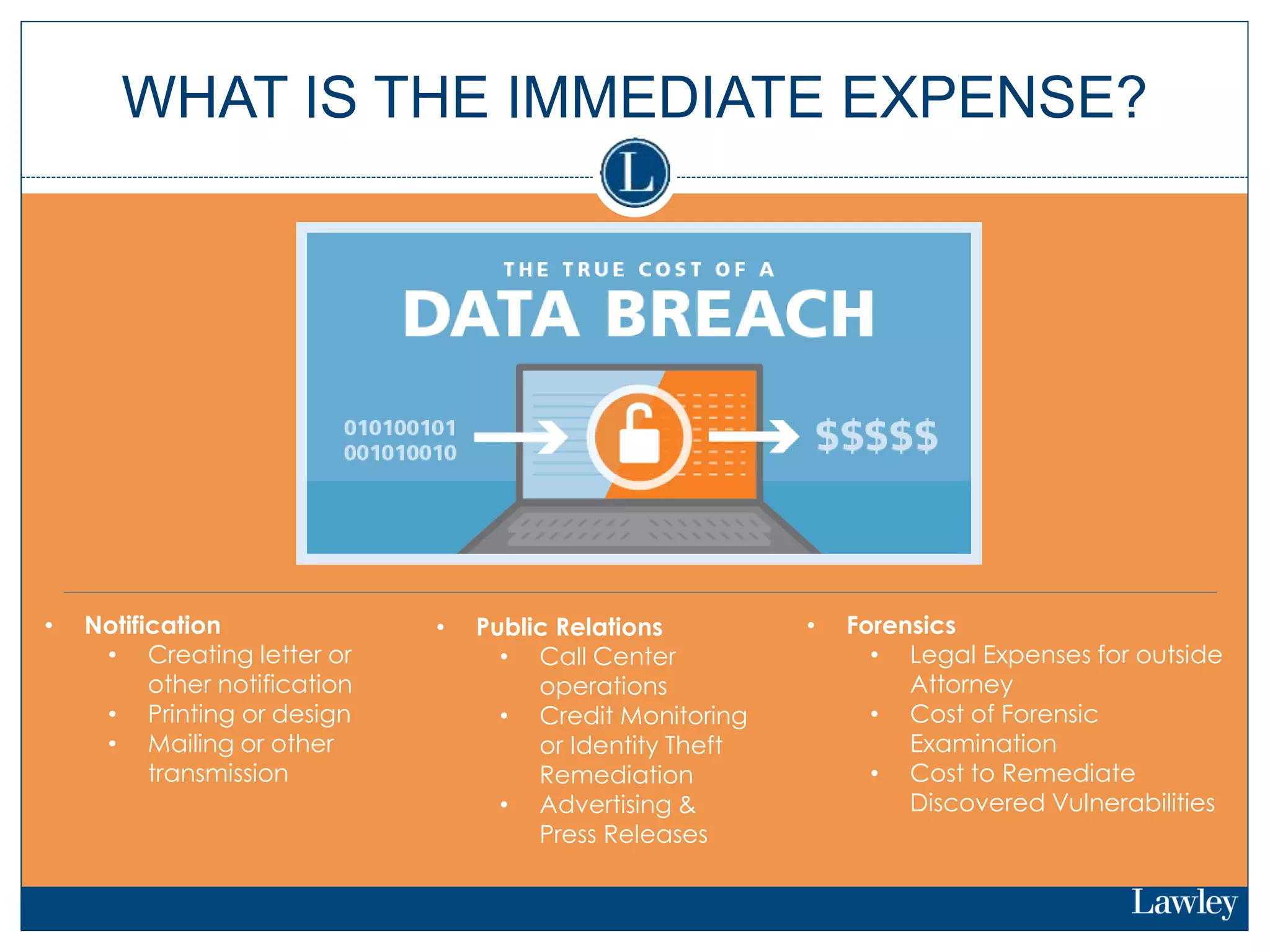
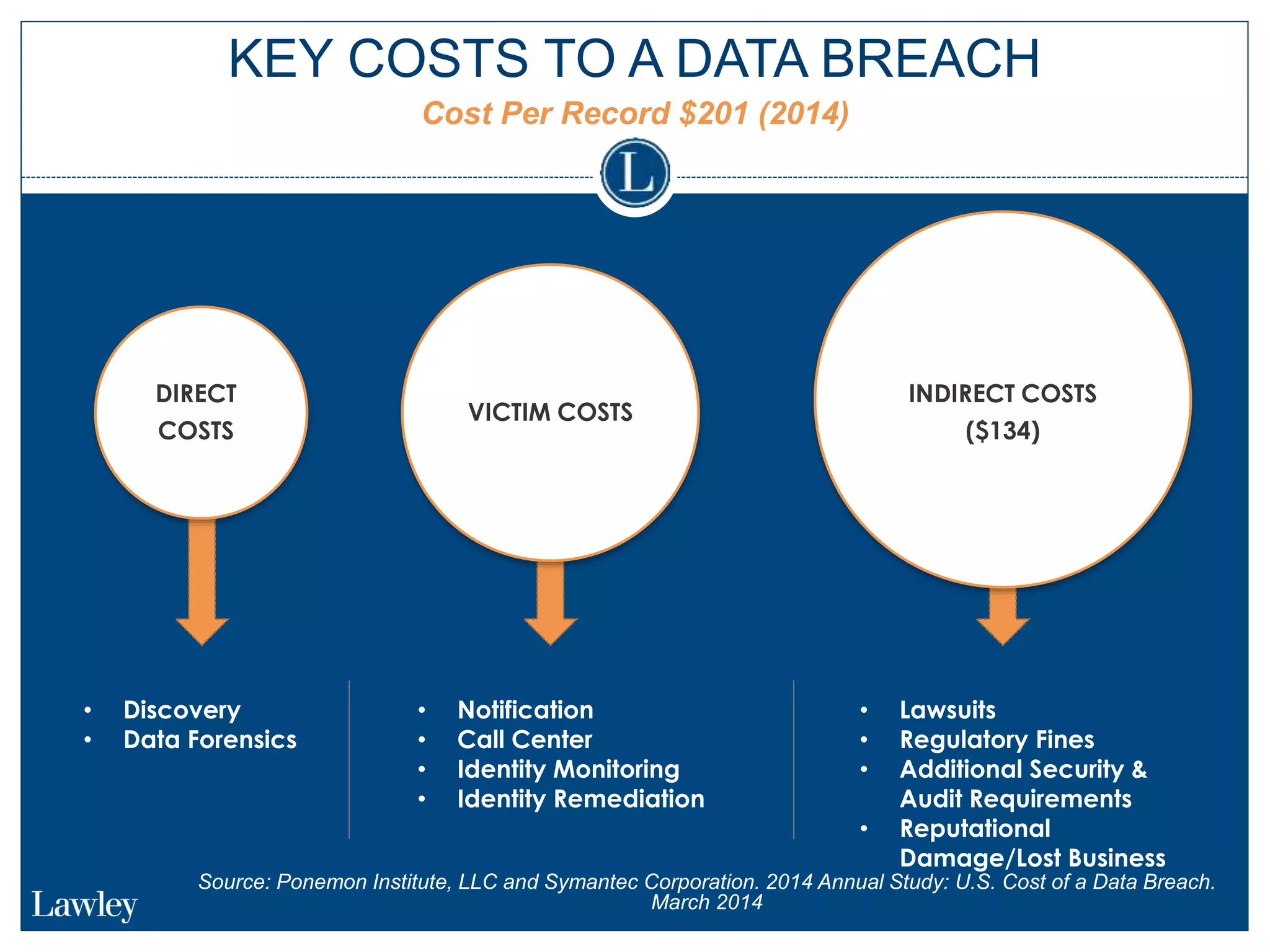
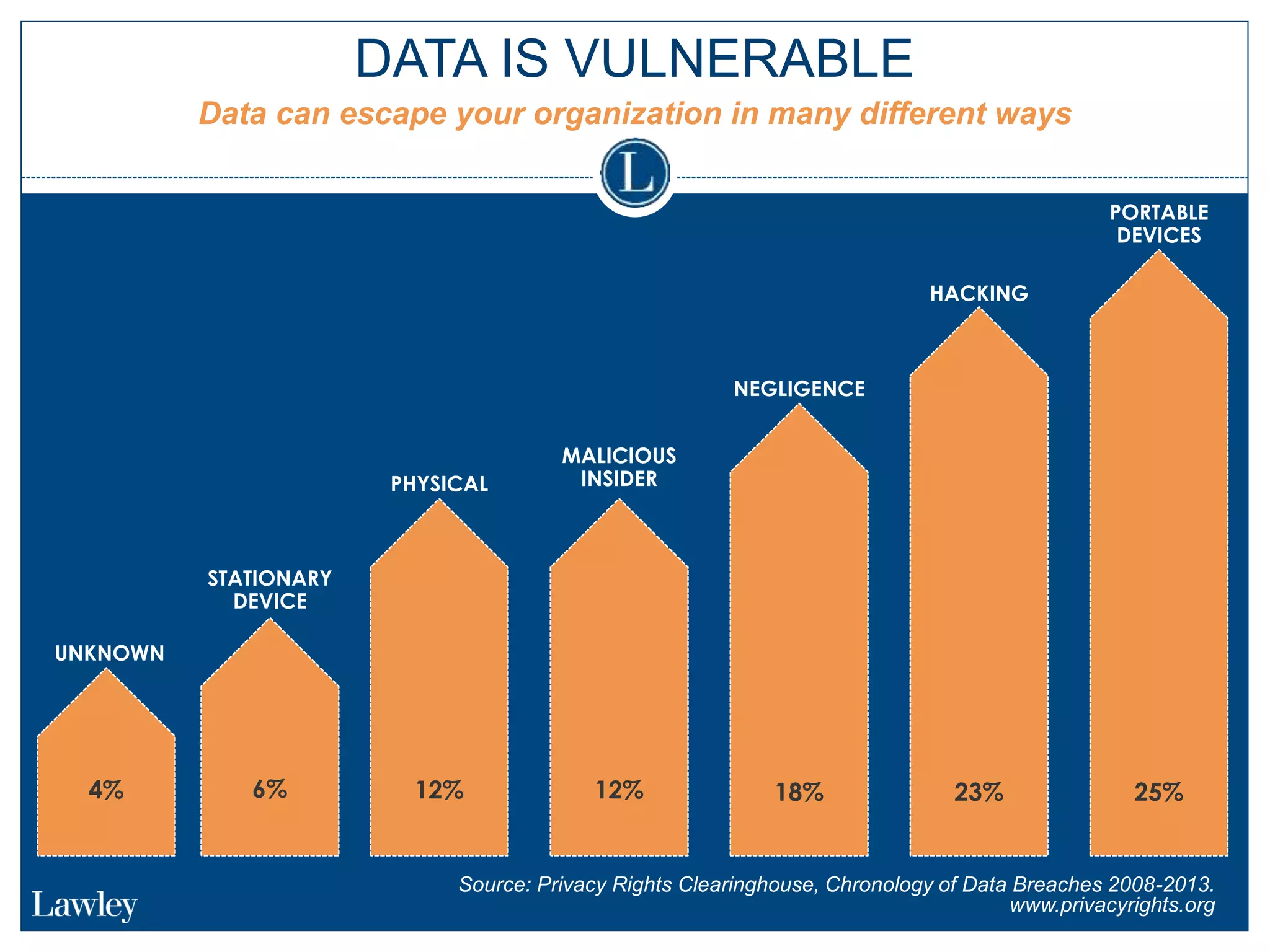
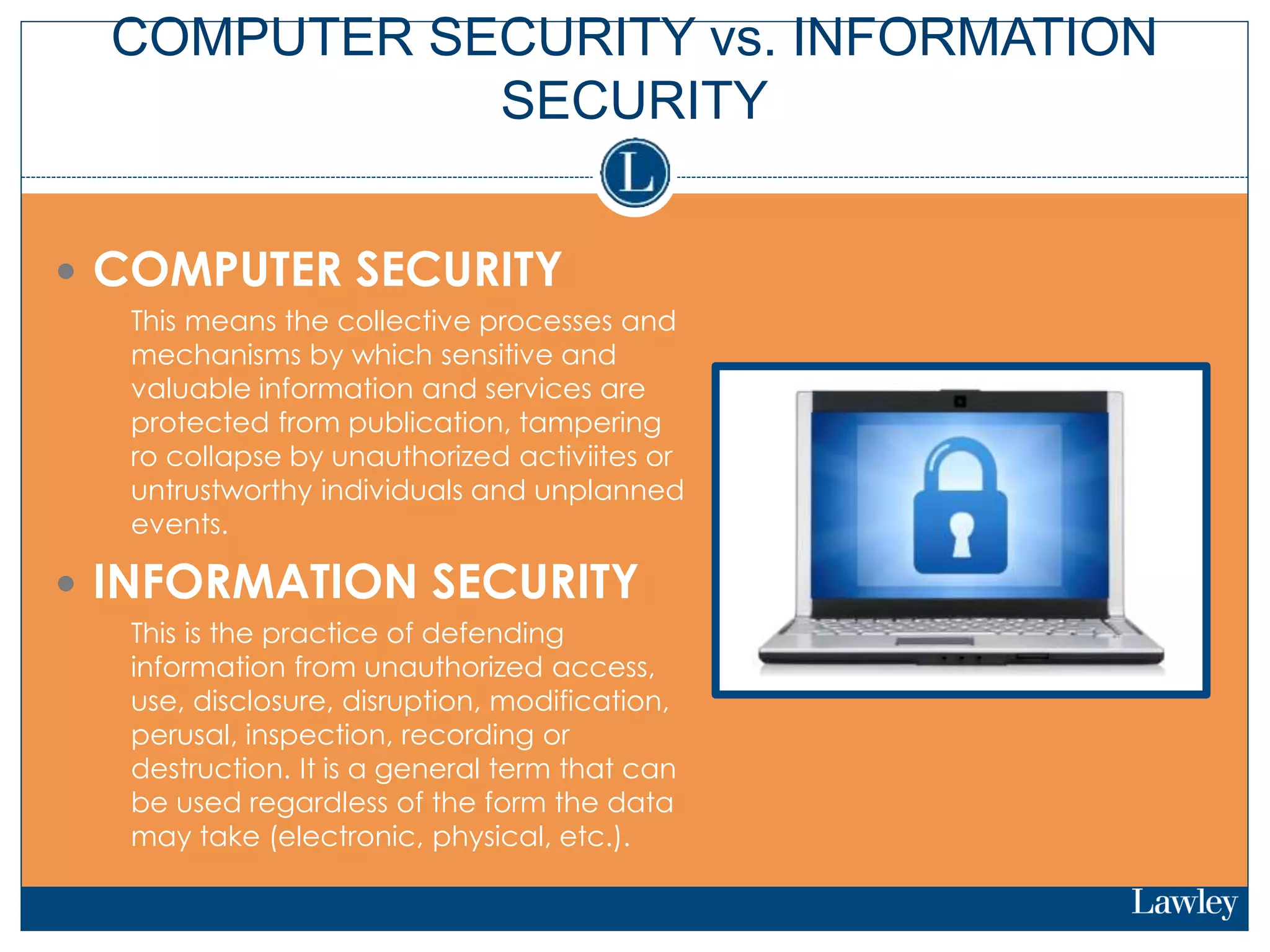
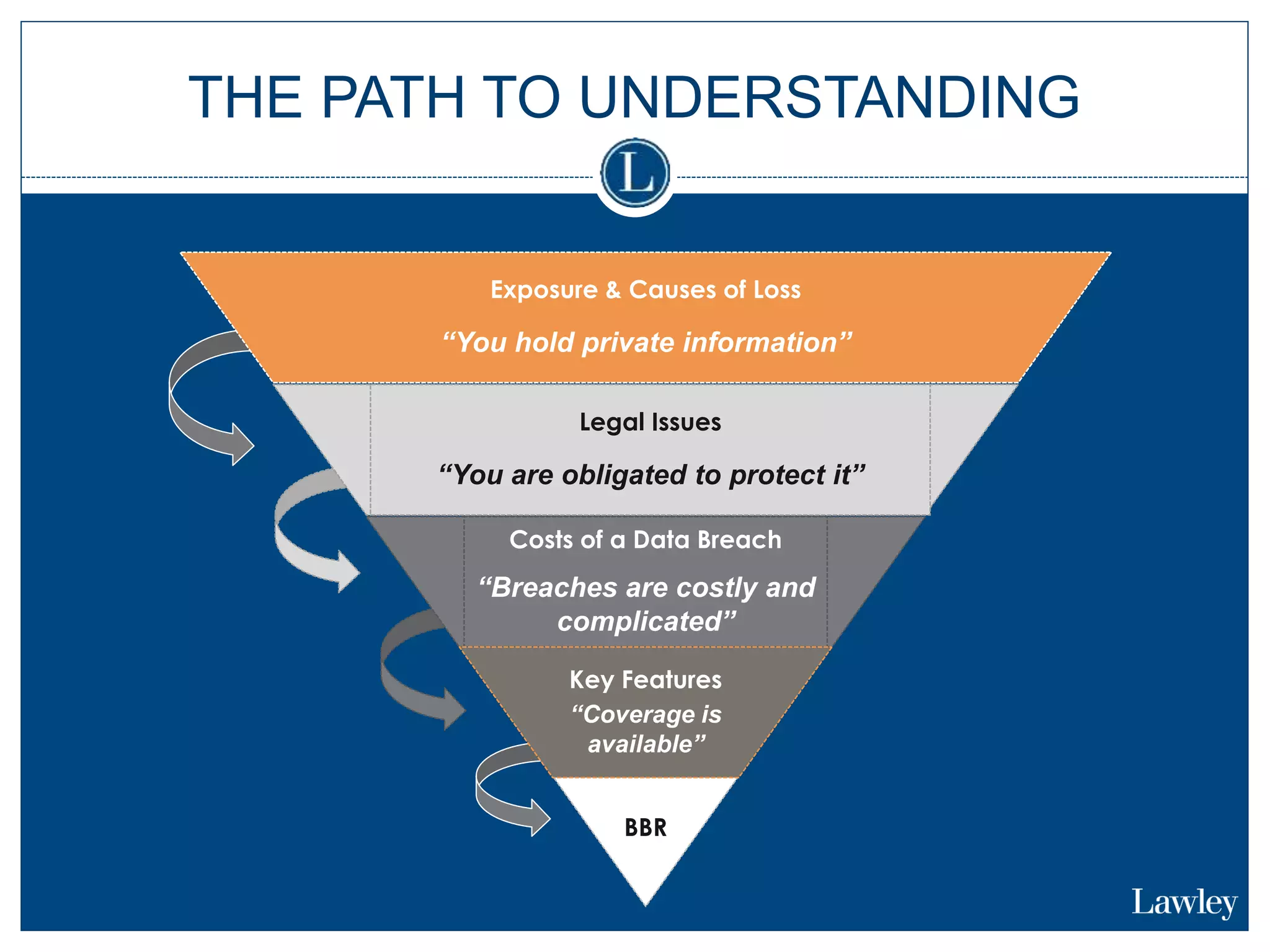
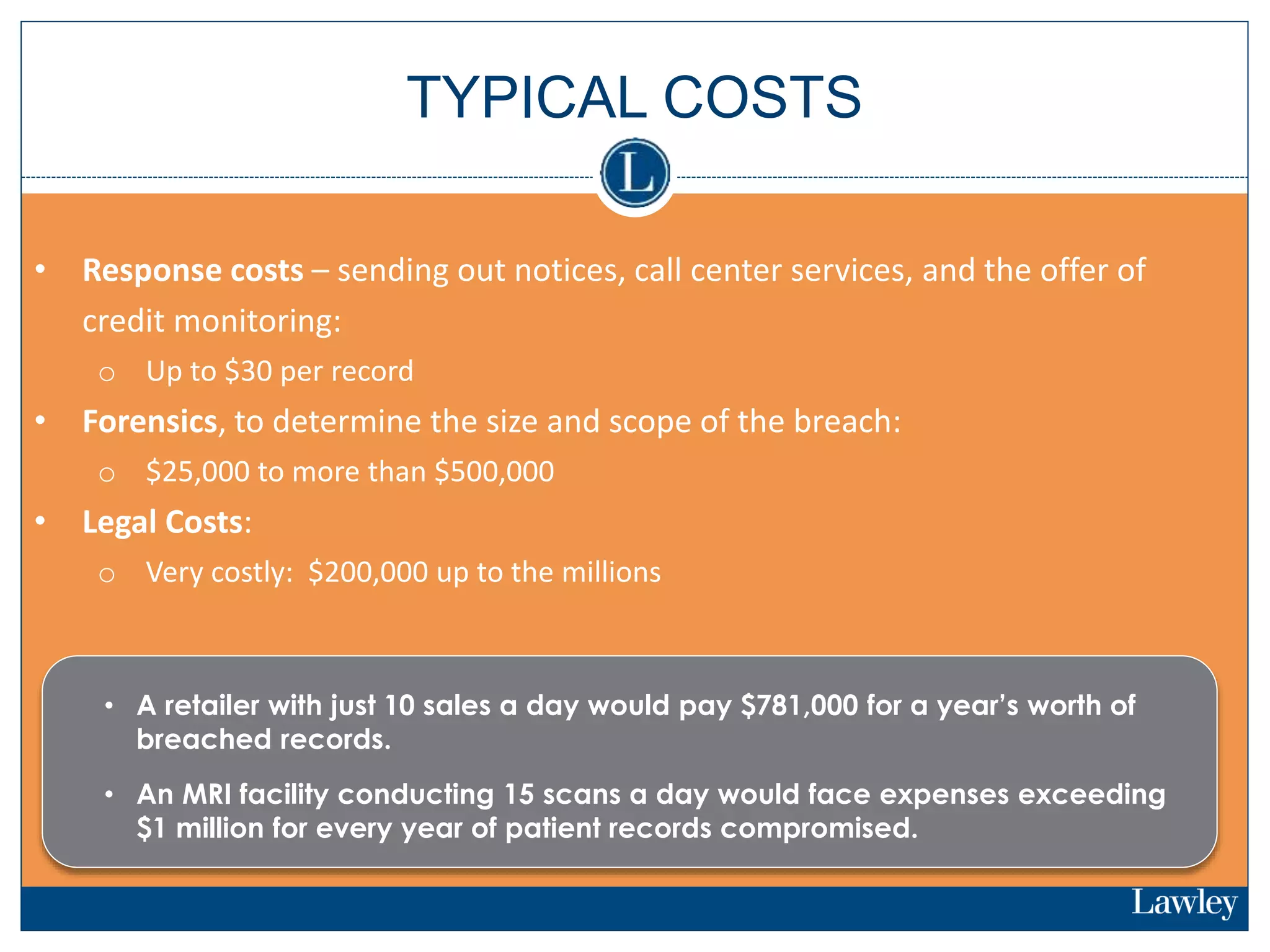
This document summarizes a seminar on cybersecurity insurance. It discusses the presenters and provides examples of data breach headlines. It then explains the threats to data, including internal and external threats. The document outlines the immediate expenses of a data breach such as notification, call centers, credit monitoring, legal expenses, and forensics. Finally, it discusses the typical costs of a data breach, which can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars depending on the size and type of breach.