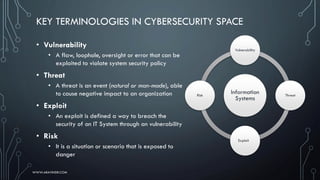
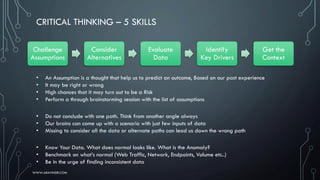
The document provides an introduction to cybersecurity, covering key concepts, historical context, and the importance of critical thinking in managing cybersecurity challenges. It discusses fundamental principles such as the CIA triad (confidentiality, integrity, availability), common security threats, and the roles of professionals in the field. Additionally, it highlights the growing demand for cybersecurity roles and the need for ongoing skills development in response to evolving threats.