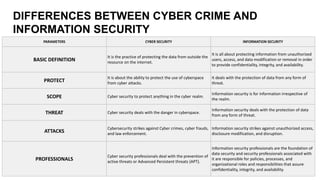
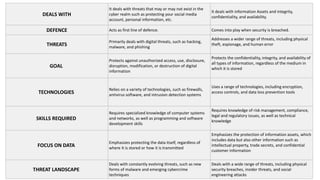
The document discusses the critical issues of cybercrime and information security in the digital age, highlighting various types of cyber threats such as phishing, malware, and cyber extortion. It emphasizes the importance of implementing robust cybersecurity measures, incident response planning, and continuous monitoring to protect sensitive data and maintain business continuity. Furthermore, it distinguishes between cybersecurity and information security, outlining the skills, technologies, and threats associated with each.