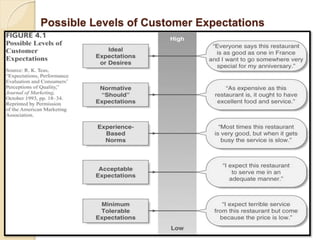
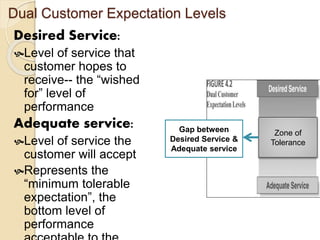
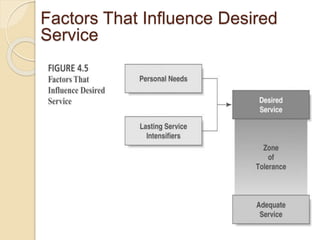
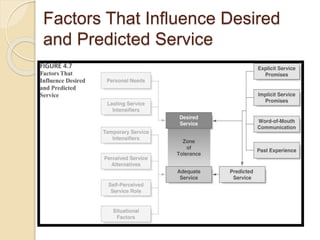
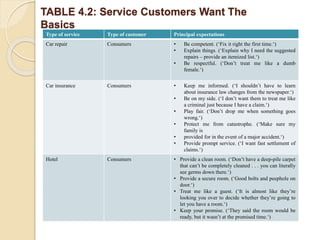
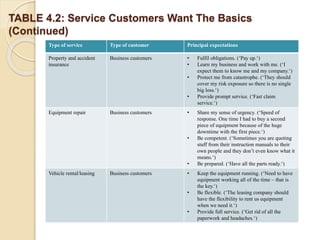
This document discusses customer service expectations. It begins by defining customer expectations and the different types or levels of expectations customers can have, including desired, adequate, and minimum tolerable expectations. It then examines factors that influence both desired expectations and adequate expectations, such as personal needs, perceived alternatives, and company communications. Finally, it discusses some current issues related to customer expectations, such as how to address unrealistic expectations, whether companies should try to exceed expectations, and if expectations continually escalate over time. The key is for companies to meet and ideally exceed customer expectations better than the competition to stay ahead.