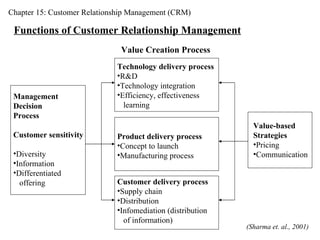
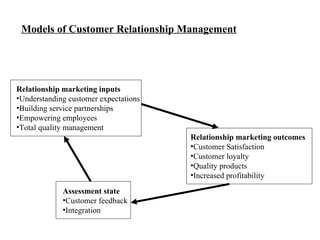
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. It involves developing mutually beneficial long-term relationships with important customers through open communication and feedback. The goal is to deliver superior customer value profitably. CRM requires identifying customer needs and building value-driven relationships to gain a competitive advantage.