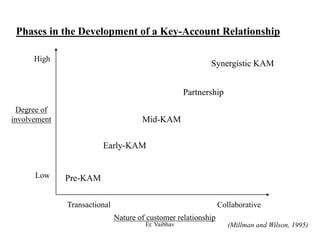
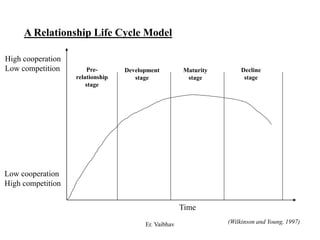
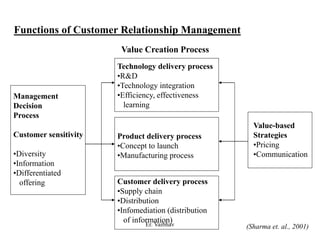
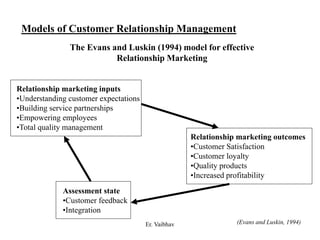
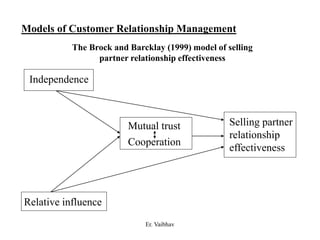
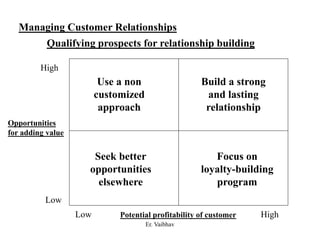
CRM aims to develop and maintain long-term relationships with customers through mutual trust and value. It involves identifying customer needs, integrating competencies to satisfy customers, and focusing on customer value over time. CRM develops through different stages from initial interactions to long-term partnerships. Salespeople play a key role in building relationships and promoting CRM strategies within organizations. The goal is superior customer value and loyalty through the customer relationship life cycle.