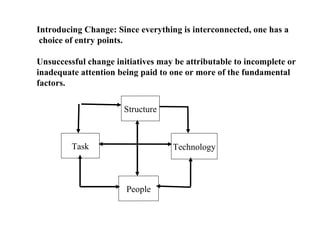
The document discusses culture and how it influences human behavior and social organization. It defines culture as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, customs, and habits acquired by people as members of society. Culture determines how basic human needs are met and influences areas like family structures, food, housing, dress, occupations, and social hierarchies. The document examines how culture shapes perception, relationships, roles, personality development, and approaches to management and leadership. It also discusses how cultural change involves conflicts as new roles and power structures emerge.