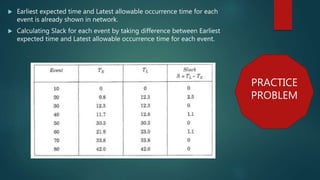
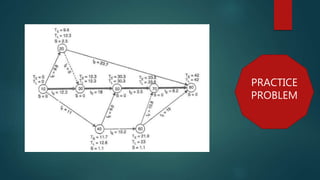
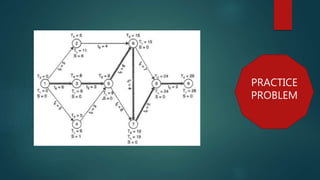
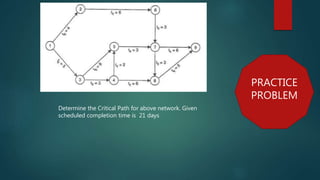
This document discusses construction project scheduling techniques including critical path method. It defines slack as the difference between earliest expected and latest allowable times, and explains that activities on the critical path with zero slack are most critical to completing the project on schedule. The document also provides steps to calculate the probability of meeting a scheduled completion date based on the critical path's standard deviation and the probability factor.