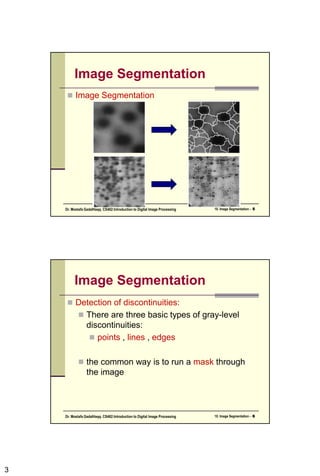
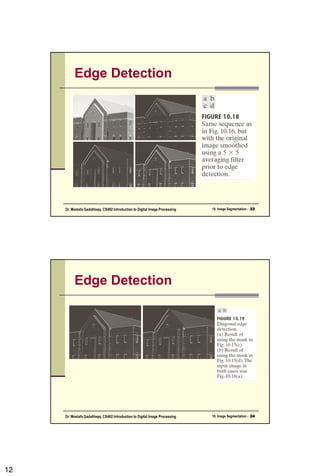
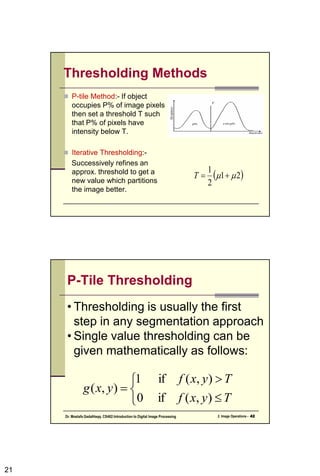
The document discusses image segmentation techniques. It describes how segmentation attempts to partition pixels into groups that correlate with image objects. The main segmentation approaches are based on discontinuities like edges or similarities within regions. Specific techniques covered include thresholding, edge detection using gradient and Laplacian operators, and the Hough transform for global line detection. Adaptive thresholding is also summarized as a method to handle uneven illumination.