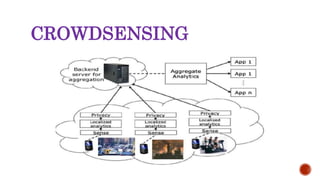
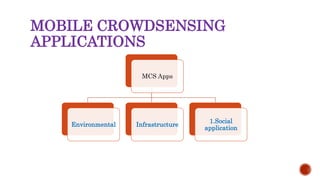
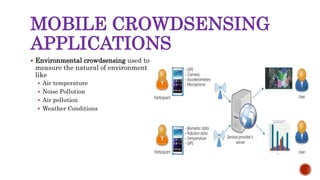
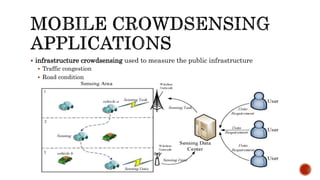
This document discusses mobile crowdsensing and its applications. It begins with an introduction to crowdsensing and the rise of sensing devices and the Internet of Things. It then describes how crowdsensing uses smartphones and other mobile devices to collect and share data. It discusses challenges like resource limitations and privacy. It also outlines potential applications in environmental monitoring, infrastructure monitoring, and social applications. It concludes by discussing future research directions such as optimization techniques and privacy protections.