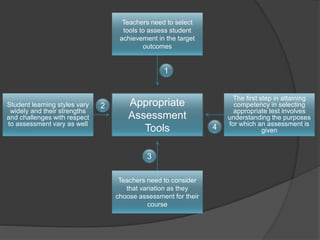
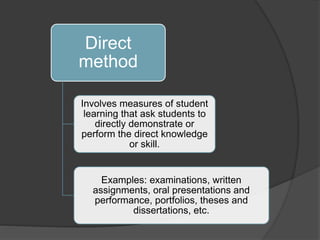
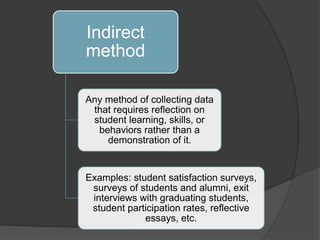
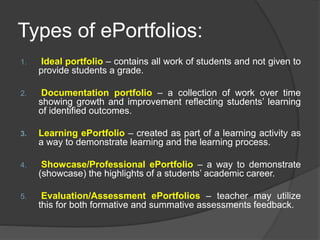
The document discusses various assessment tools and methods that teachers can use to evaluate student learning and achievement. It examines direct assessment methods like exams and assignments that require students to demonstrate skills and knowledge. It also looks at indirect methods like surveys that collect student feedback. The document provides details on rubrics, electronic exams, paper-and-pencil tests, and electronic portfolios as specific assessment options. It emphasizes the importance of teachers selecting tools that accurately measure intended outcomes and provide useful feedback to improve learning.