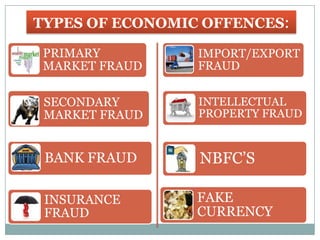
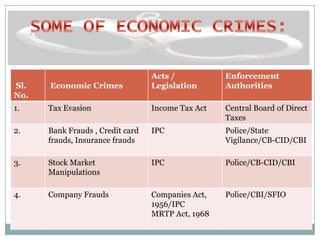
The document discusses various types of economic offenses in India such as bank fraud, stock market manipulation, money laundering, and more. It provides examples of major scams that have occurred, including the Harshad Mehta stock market scam from 1992, the Ketan Parekh scam from 2001, the fake stamp paper scam by Abdul Karim Telgi, and the 2G spectrum scam involving A. Raja and others. The roles of regulatory authorities for economic crimes like SEBI and acts like the Prevention of Money Laundering Act are also summarized.