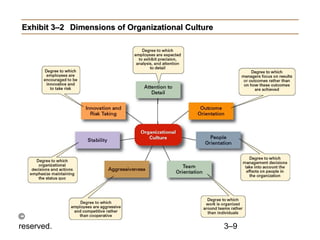
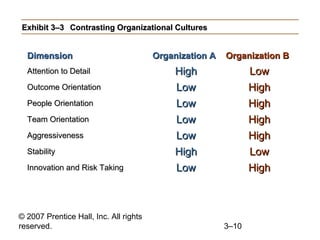
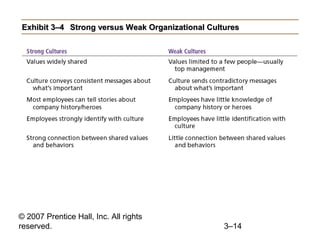
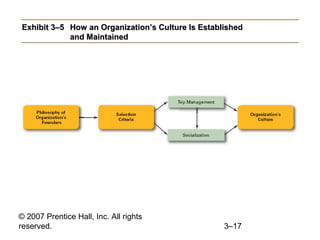
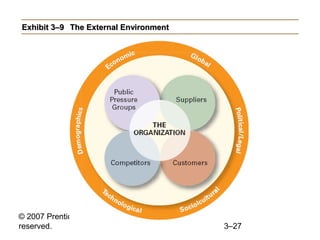
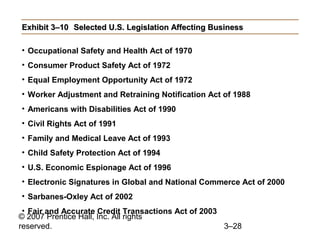
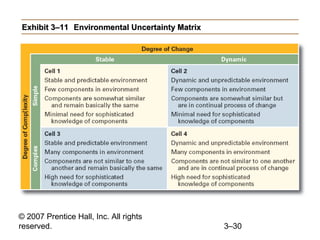
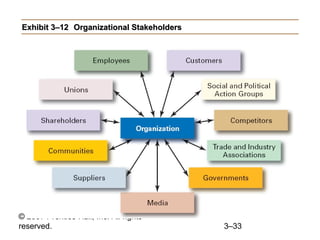
This document provides an overview of organizational culture and the external environment as constraints on managers according to Chapter 3 of the textbook. It defines key terms like organizational culture, describes the seven dimensions of culture, and explains how culture is established and influences managers' decisions. It also discusses the external environment and how factors like complexity and change can create uncertainty for managers. The document outlines steps for managing stakeholder relationships.