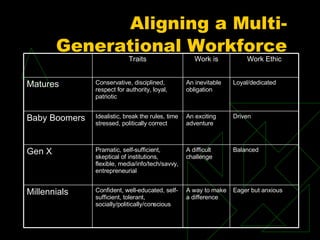
The document discusses the dynamics of resistance to organizational change, emphasizing how focusing on technical aspects while ignoring human elements can hinder progress. It outlines various causes and behaviors of resistance, along with strategies for managing it, such as communication, participation, and team-building. Additionally, it highlights the challenges of a multi-generational workforce and the importance of understanding diverse perspectives in facilitating effective change.