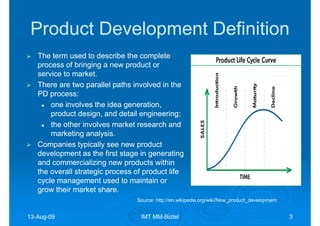
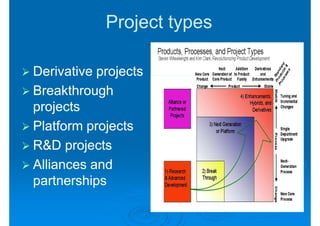
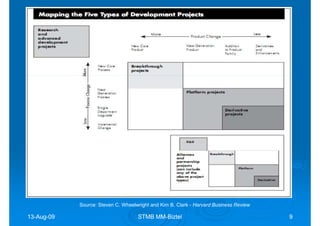
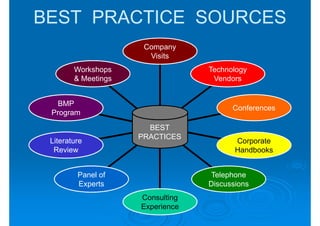
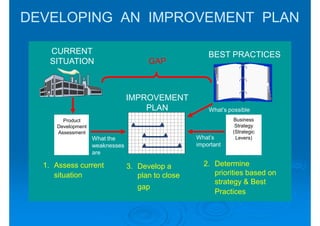
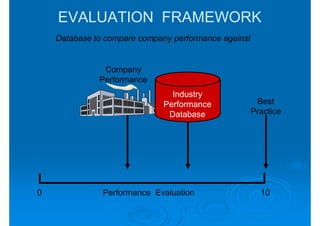
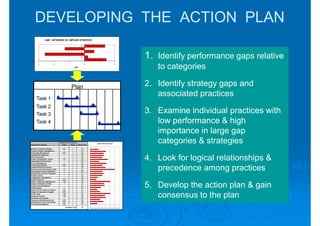
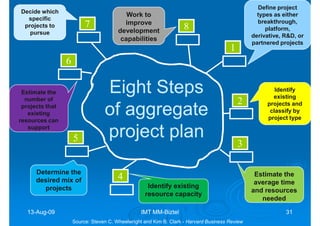
The document discusses building competencies through new product development and creating project plans to focus product development efforts. It describes how PreQuip, a scientific instruments company, lacked an aggregate project plan, leading to too many projects and decreased productivity. The presentation recommends categorizing projects into types like derivative or breakthrough, and using an aggregate plan to reduce projects and focus on those strategically important. It also discusses defining product and project success, with product success depending on meeting strategic goals and user needs.