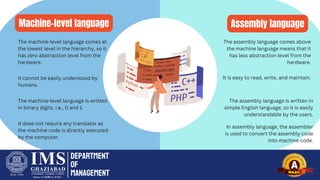
The document provides an overview of programming languages, categorizing them into low-level (machine language and assembly language) and high-level languages (like Python, Java, C++). Low-level languages offer no abstraction from hardware, making them less portable, while high-level languages are designed to be user-friendly, machine-independent, and closer to human language. The document also discusses the differences and advantages of each language category, including the execution speed and ease of code maintenance.