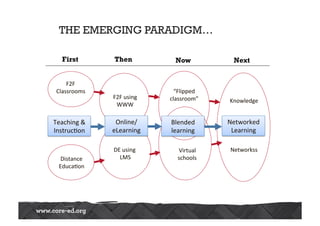
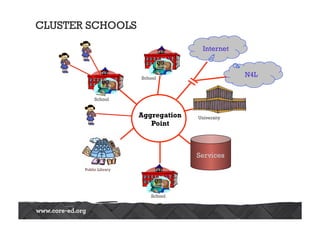
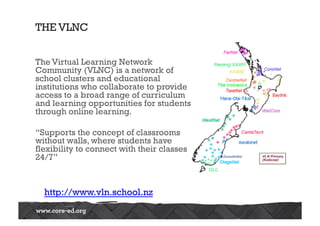
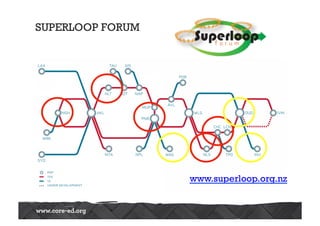
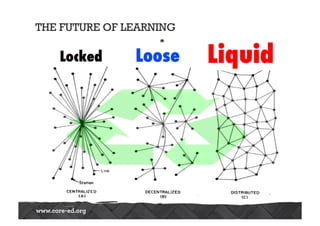
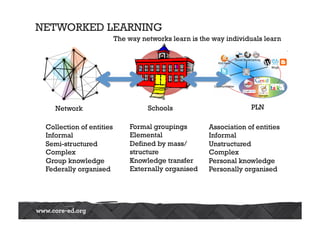
The Australasian Association of Distance Education Schools' 2013 conference explored the future of learning in a networked world, emphasizing the need for a shift from teacher-centered classrooms to learner-focused environments. It highlighted the importance of agency, personalization, and adaptability in education, alongside the integration of technology to enhance learning experiences. The conference also addressed challenges related to open content, network literacies, and the evolving landscape of distance education, suggesting that institutions must adapt to meet new learner expectations.