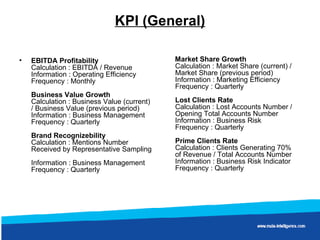
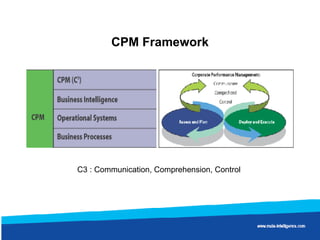
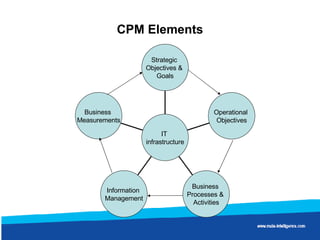
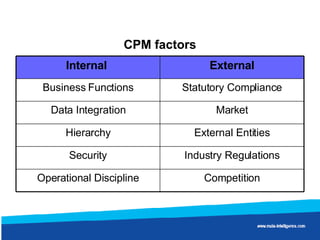
Wal-Mart discovered through data mining that sales of diapers and beer were correlated on Friday nights. It found men were being asked to pick up diapers on their way home from work. On Fridays, men would buy beer for the trouble of getting diapers. By moving diapers and beer closer together in stores, Wal-Mart saw significantly increased sales of both products.