Embed presentation
Download to read offline




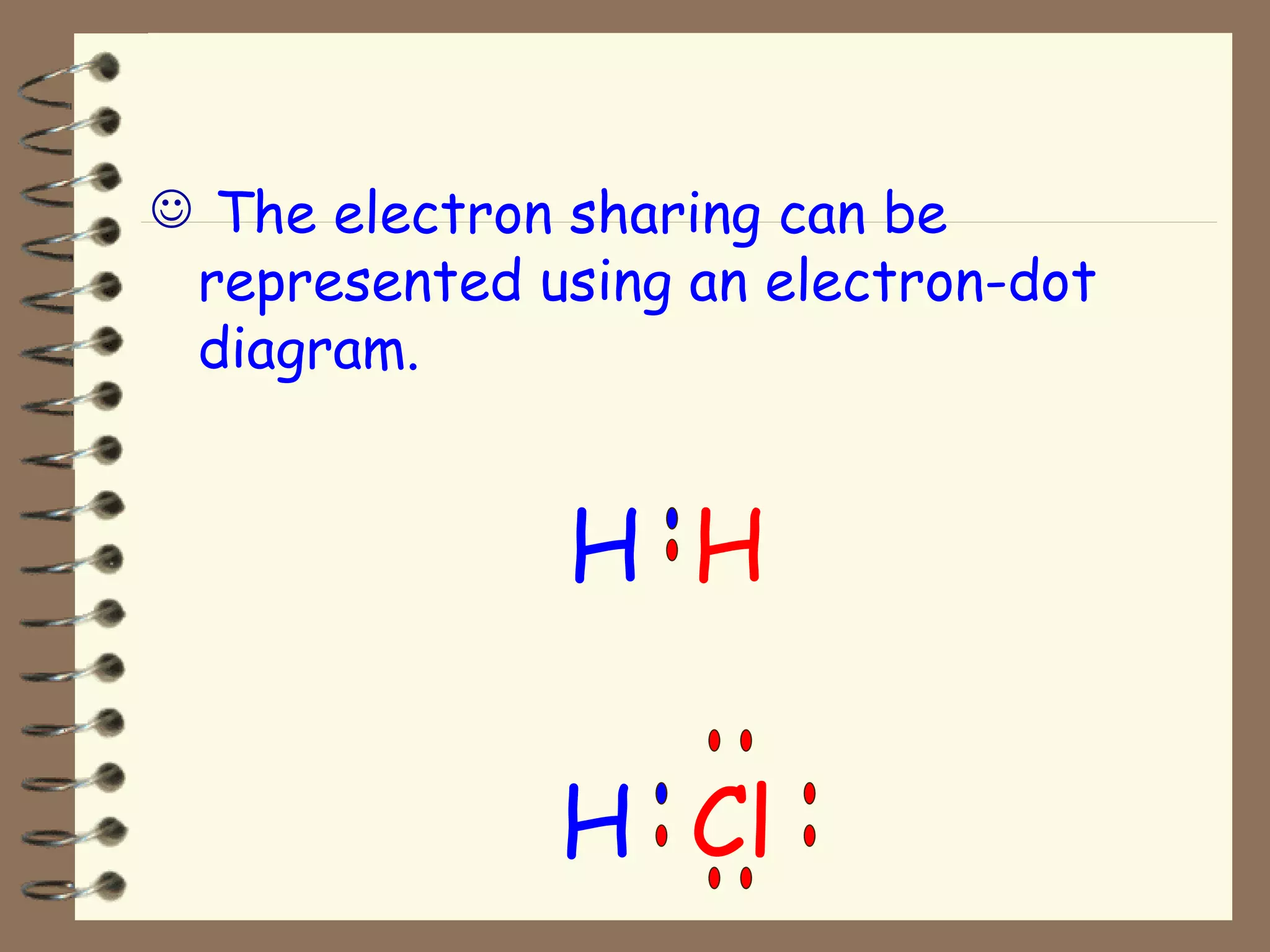
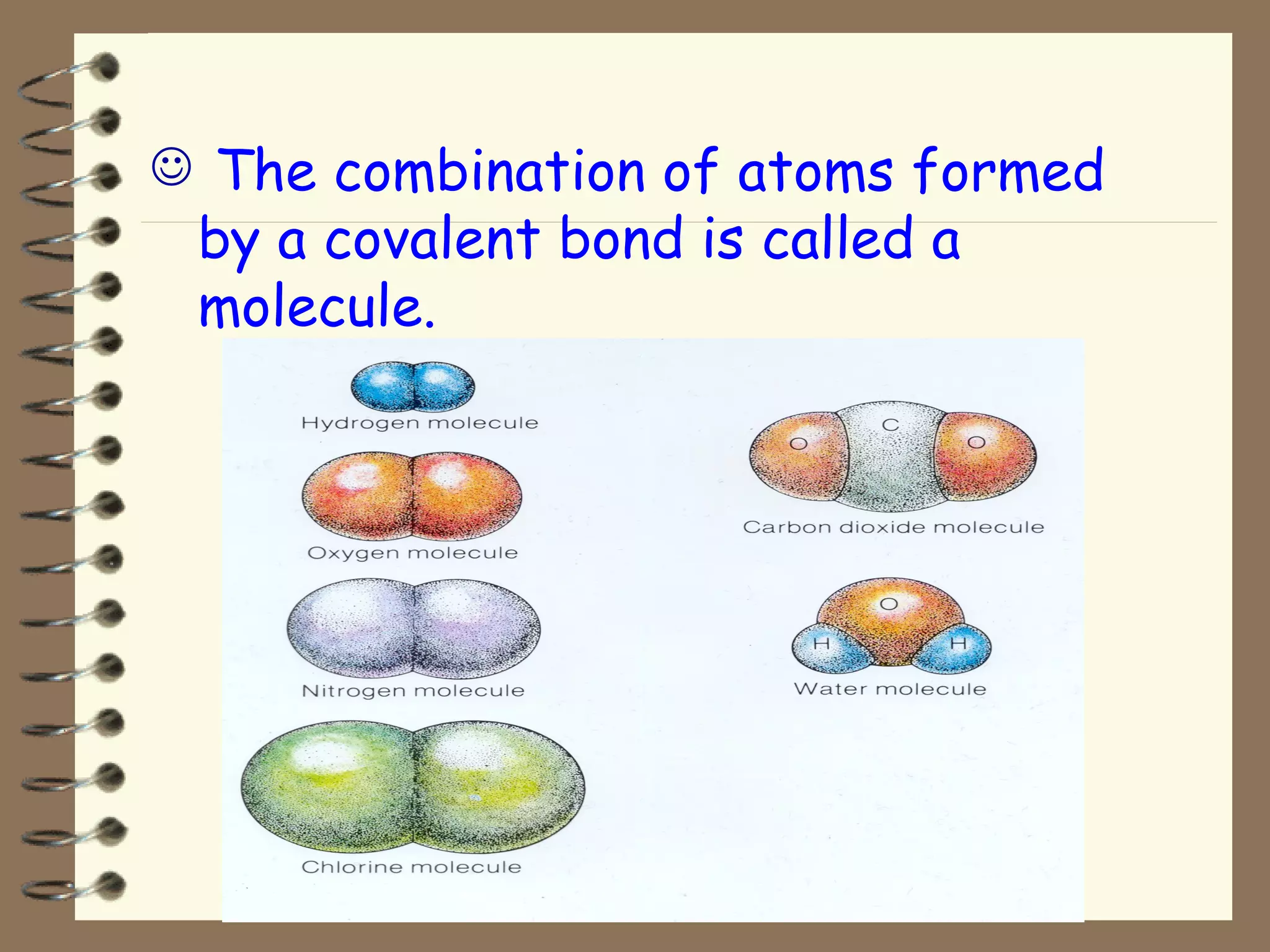

Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons to achieve a full outer shell, giving the molecule an overall charge of zero. Hydrogen always forms covalent bonds because it has only one electron to share. Examples of covalent bonds include hydrogen gas (H2) and hydrogen chloride (HCl), which can be represented using electron-dot diagrams showing the shared electrons. Molecules are combinations of atoms held together by covalent bonds, such as polyatomic ions.






