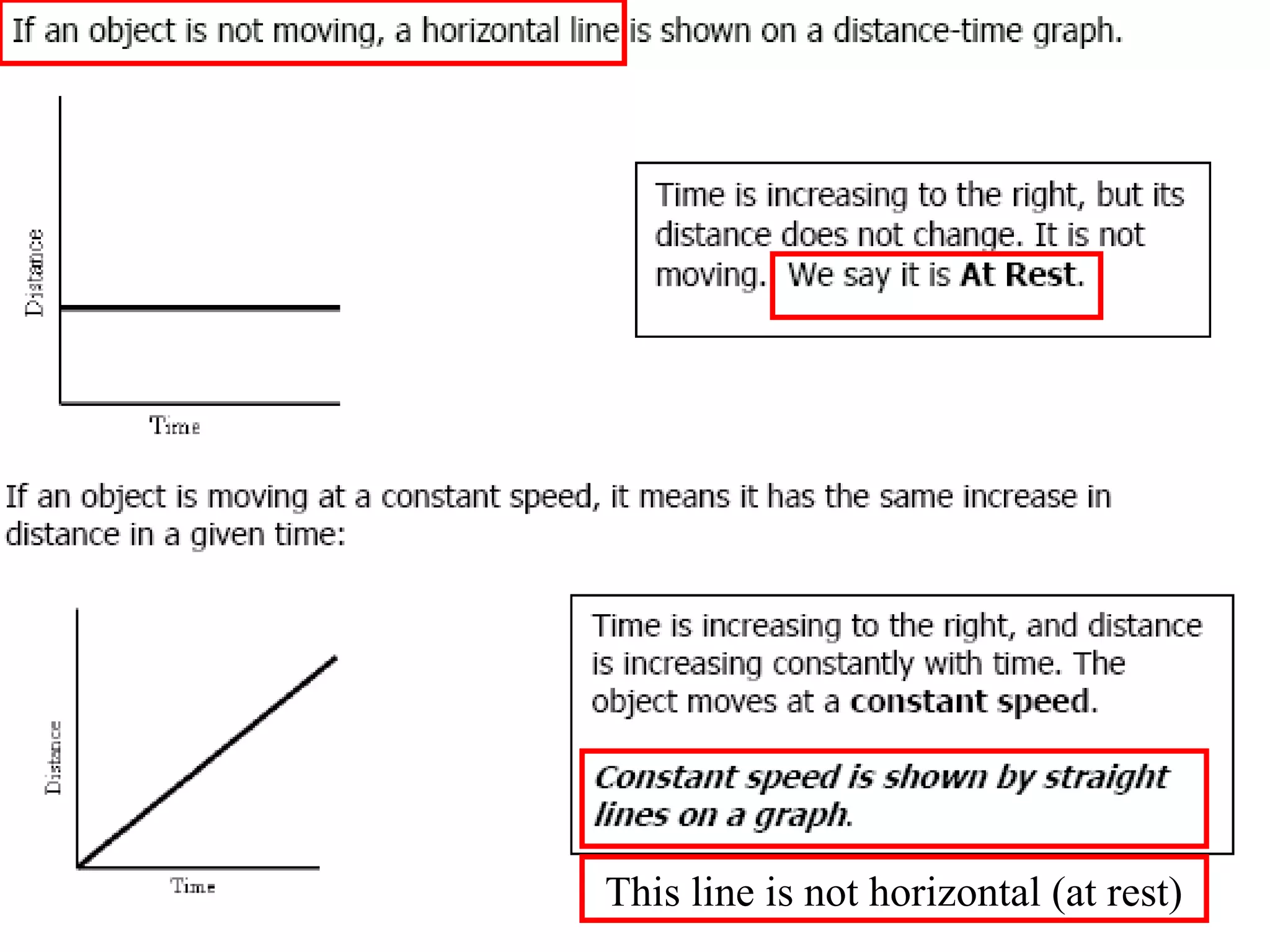
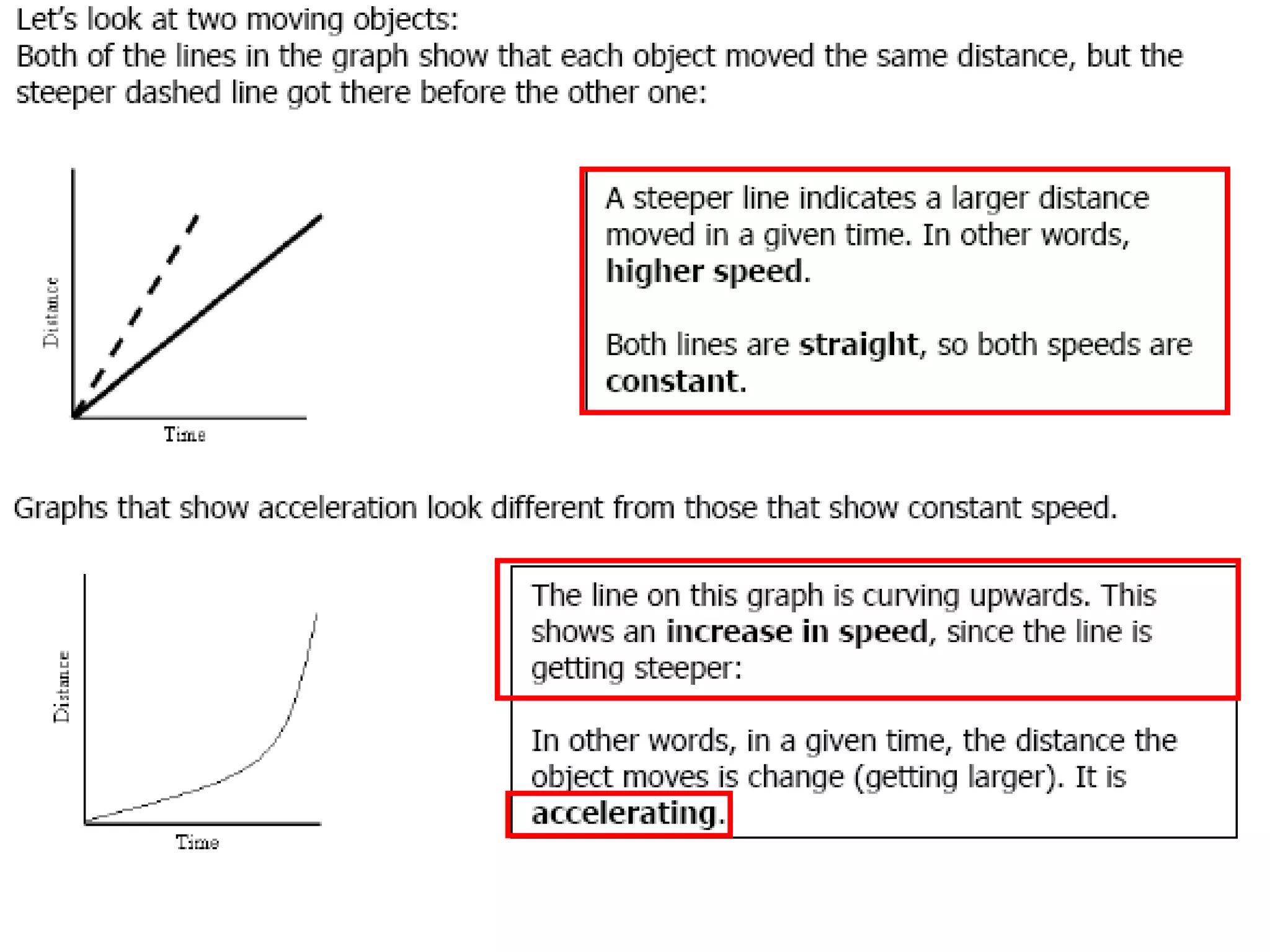
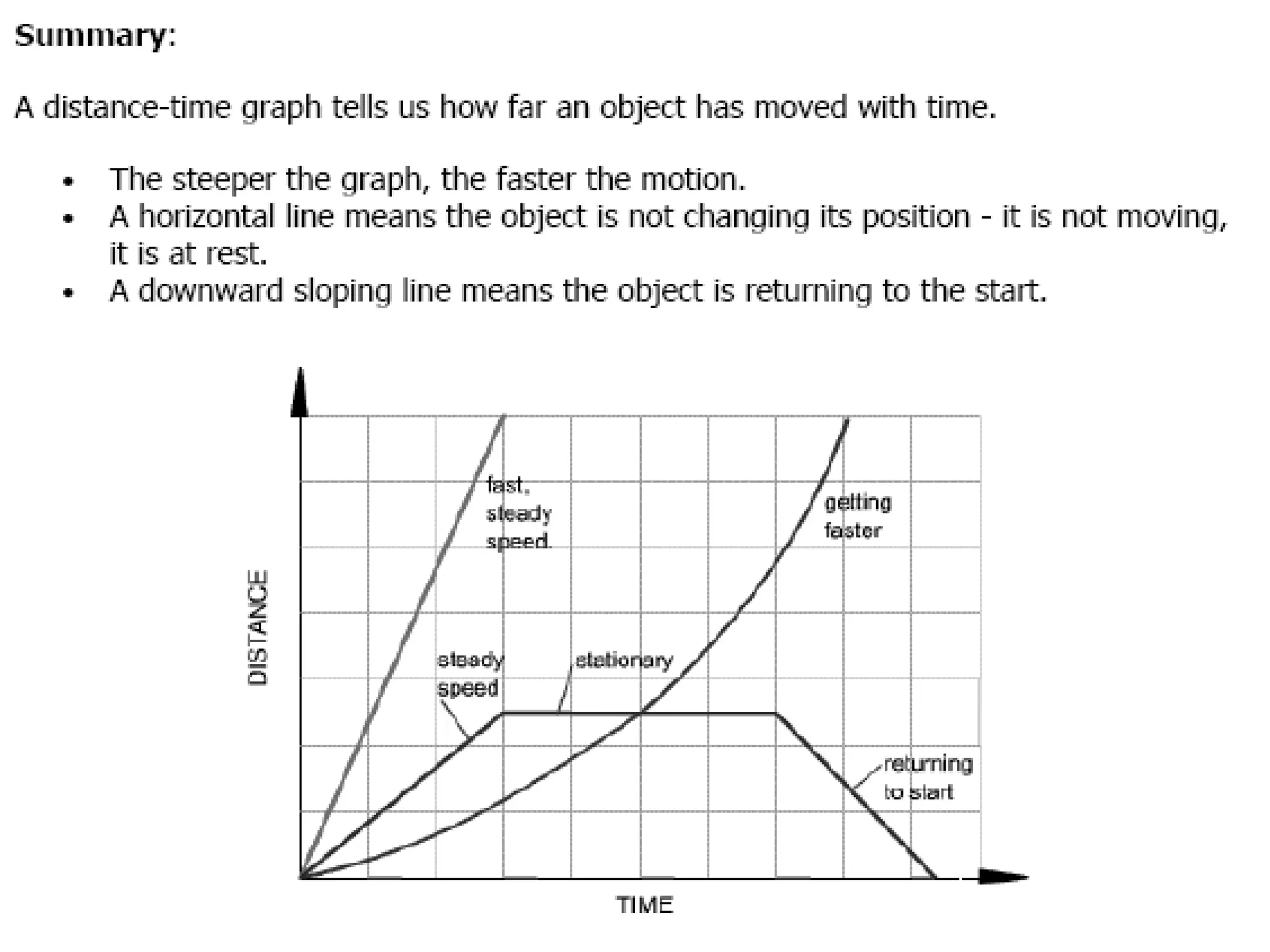
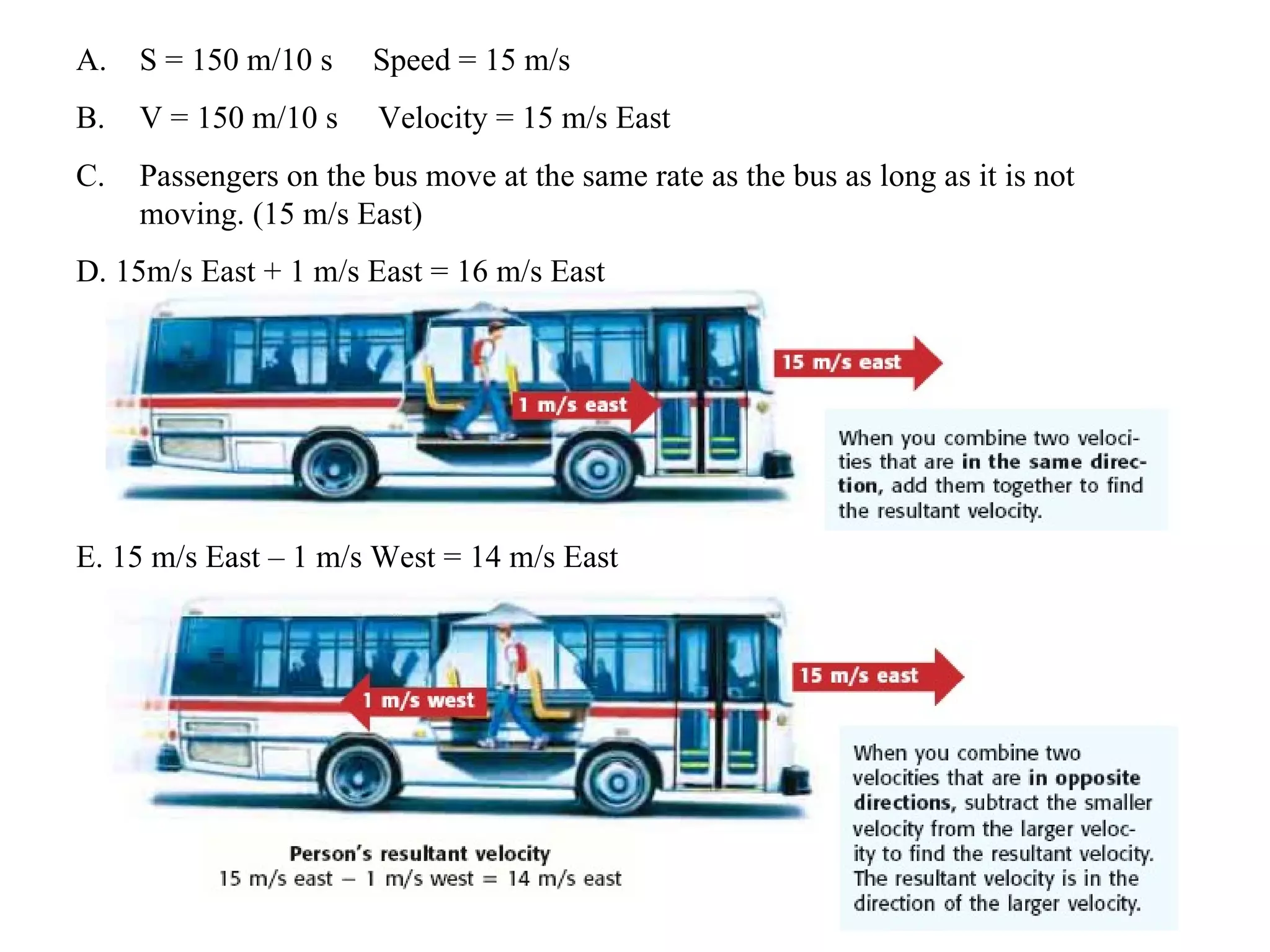
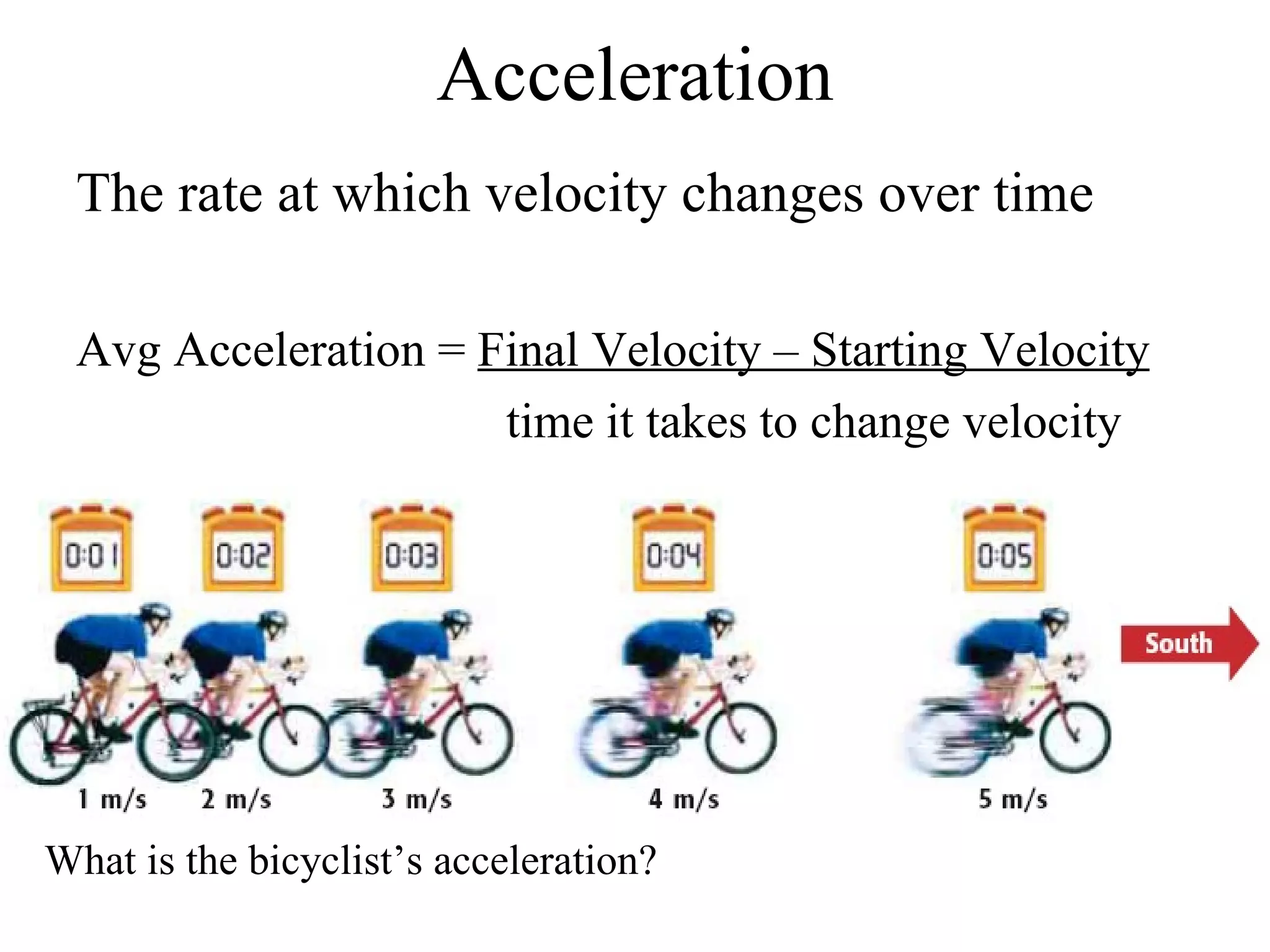
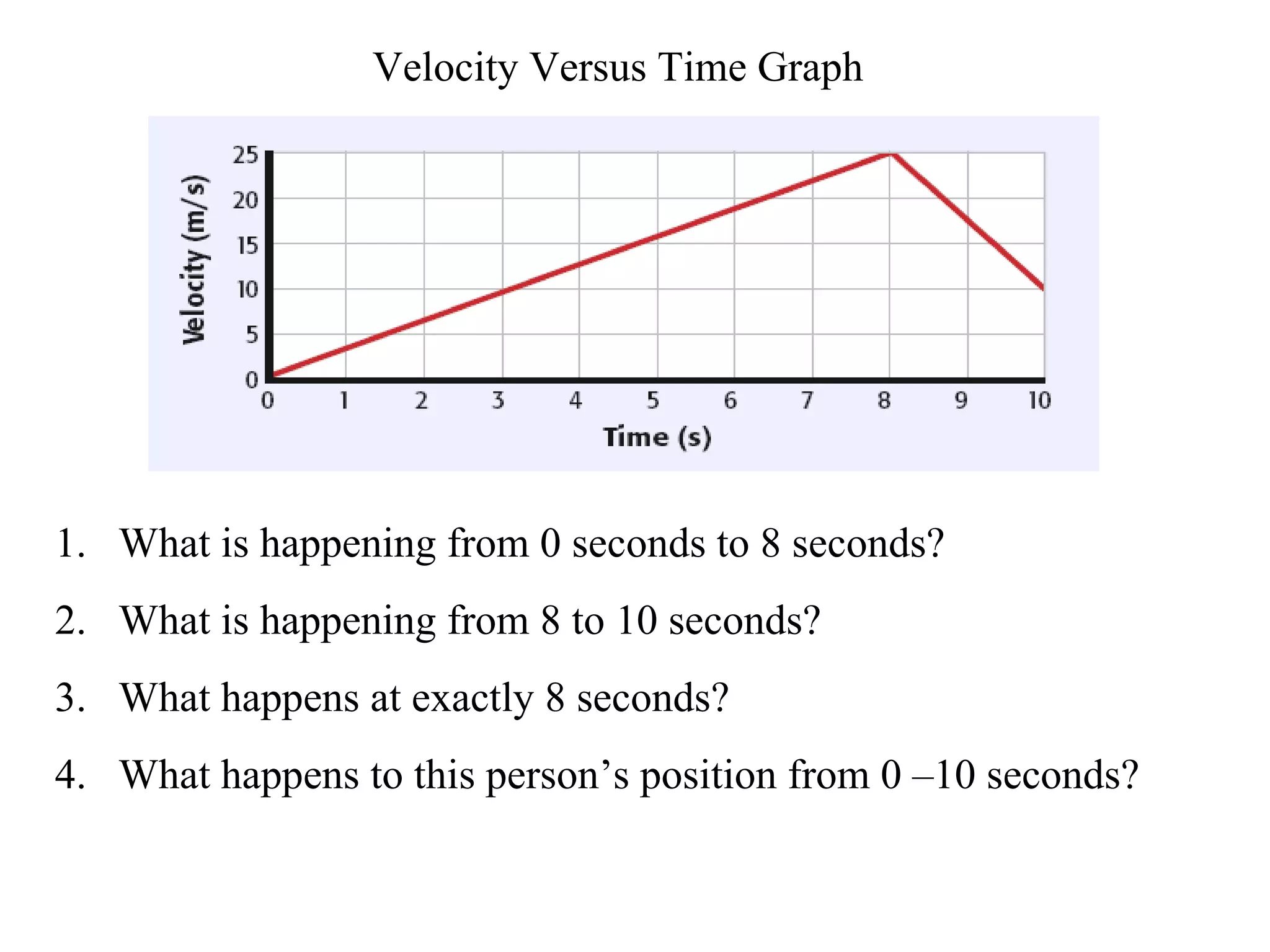
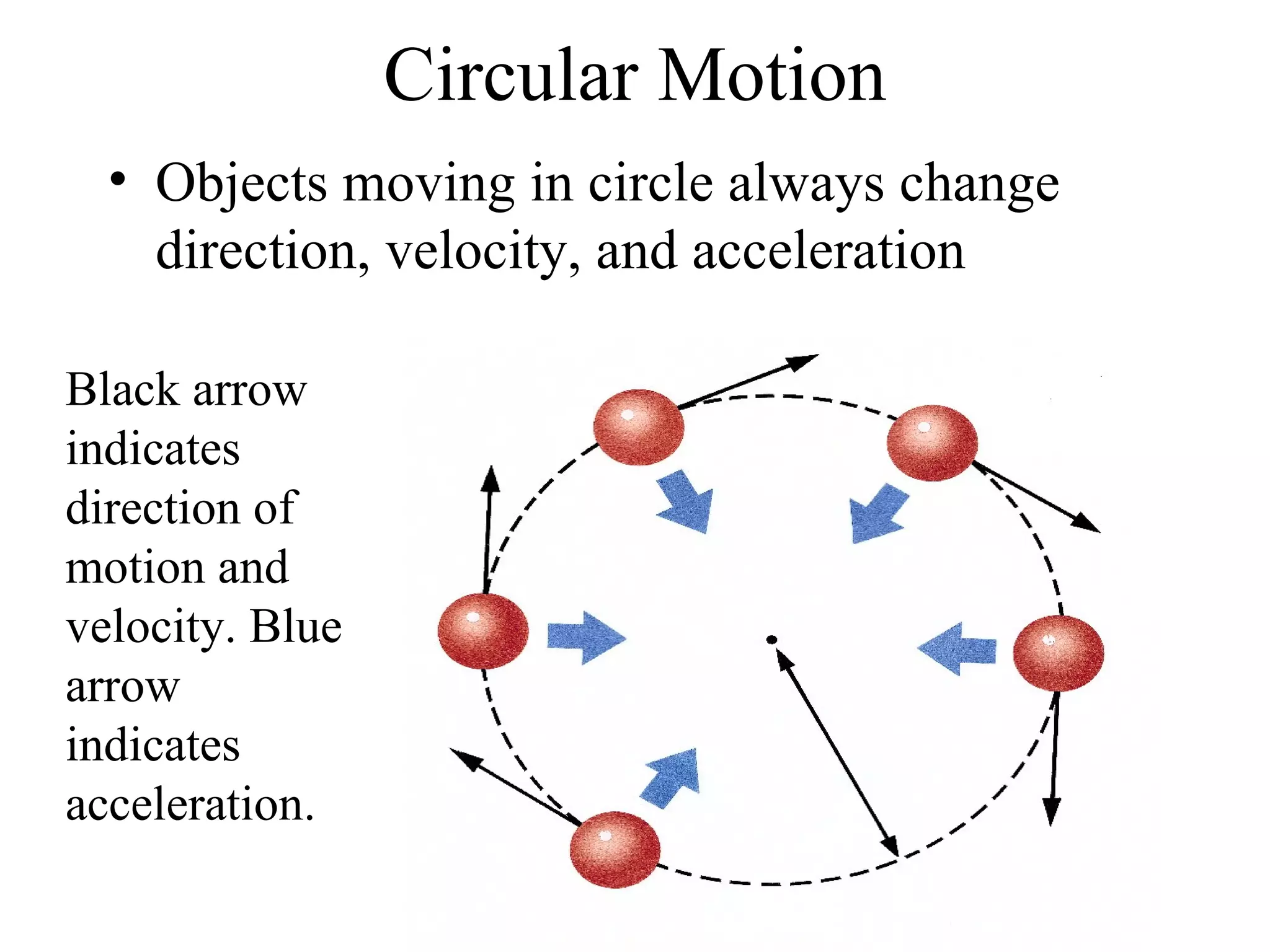
This document discusses motion and related concepts like speed, velocity, and acceleration. It defines motion as an object's change in position relative to a reference point over time. Speed is the rate of change of distance over time, while velocity also includes direction. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity over time. Examples are provided to illustrate calculating speed, velocity, and changes in velocity.