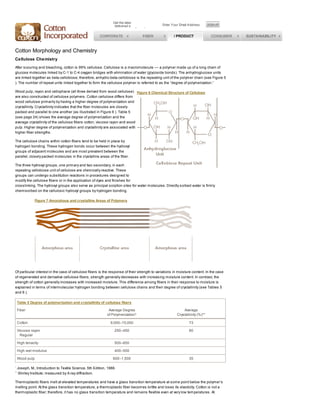
After scouring and bleaching, cotton fibers are 99% cellulose. Cellulose is a polymer made of glucose molecules linked together. Cotton cellulose has a higher degree of polymerization and crystallinity than wood cellulose. This gives cotton higher strength. The cellulose chains in cotton are held together by hydrogen bonds, especially in crystalline areas. Crystallinity and hydrogen bonding explain why cotton strength increases with moisture while other fibers decrease in strength. Cotton has a unique fiber structure of multiple layers that gives it absorbency and wicking properties. Higher micronaire cotton tends to have lower nep content after processing.