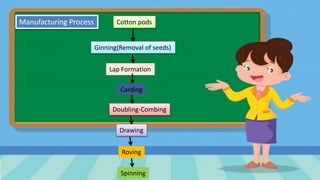
The document outlines the manufacturing process of cellulose fibers, focusing extensively on cotton, its cultivation, and properties. Cotton is hailed as a critical natural fiber globally, with significant production concentrated in regions like the United States and India. It details the physical, thermal, chemical, and biological properties of cotton, as well as its diverse applications in home furnishings, industrial uses, and apparel.