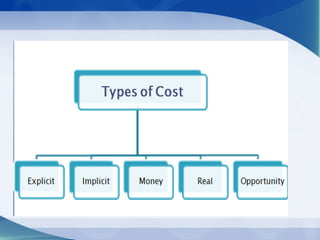
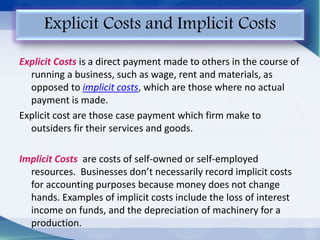
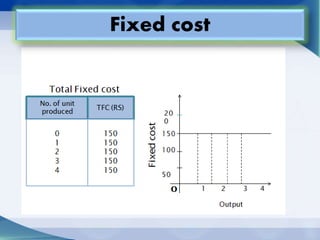
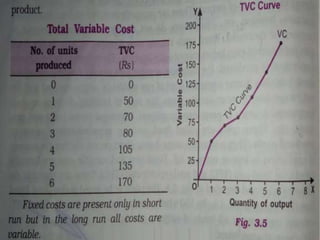
The document addresses key economic concepts related to the market, including the purchasing of commodities, methods of transaction, and price determination based on production costs. It distinguishes between explicit costs (direct payments) and implicit costs (non-monetary expenses), alongside explanations of money costs and real costs in production. Additionally, it highlights short-run costs, consisting of fixed and variable costs, with examples and definitions provided for clarity.