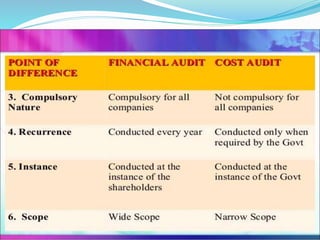
Cost audit is the verification of cost accounts and adherence to the cost accounting plan. It has several functions including verifying proper maintenance of cost accounts, detecting errors and preventing fraud. There are two aspects of cost audit - propriety audit which examines executive actions and efficiency audit which appraises performance. Advantages of cost audit are detection of issues, more reliable data, and improved cost control and productivity. In India, certain companies must maintain cost accounts and the government can order cost audits to be conducted by qualified cost accountants. Management audit evaluates management performance and assesses whether objectives are fulfilled through a review of plans, policies, and operations. It aims to improve efficiency, profitability, and ensure optimal resource utilization.