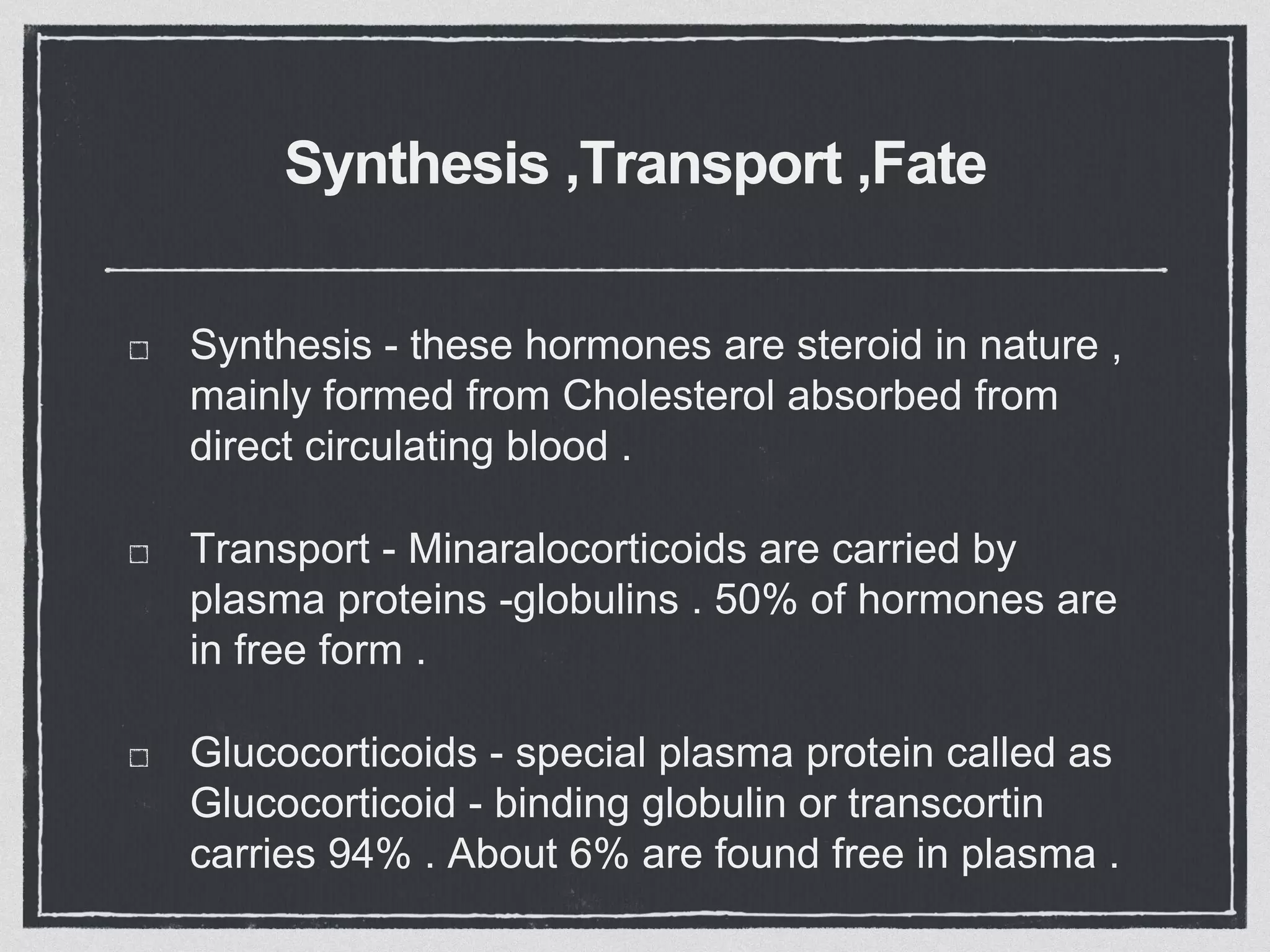
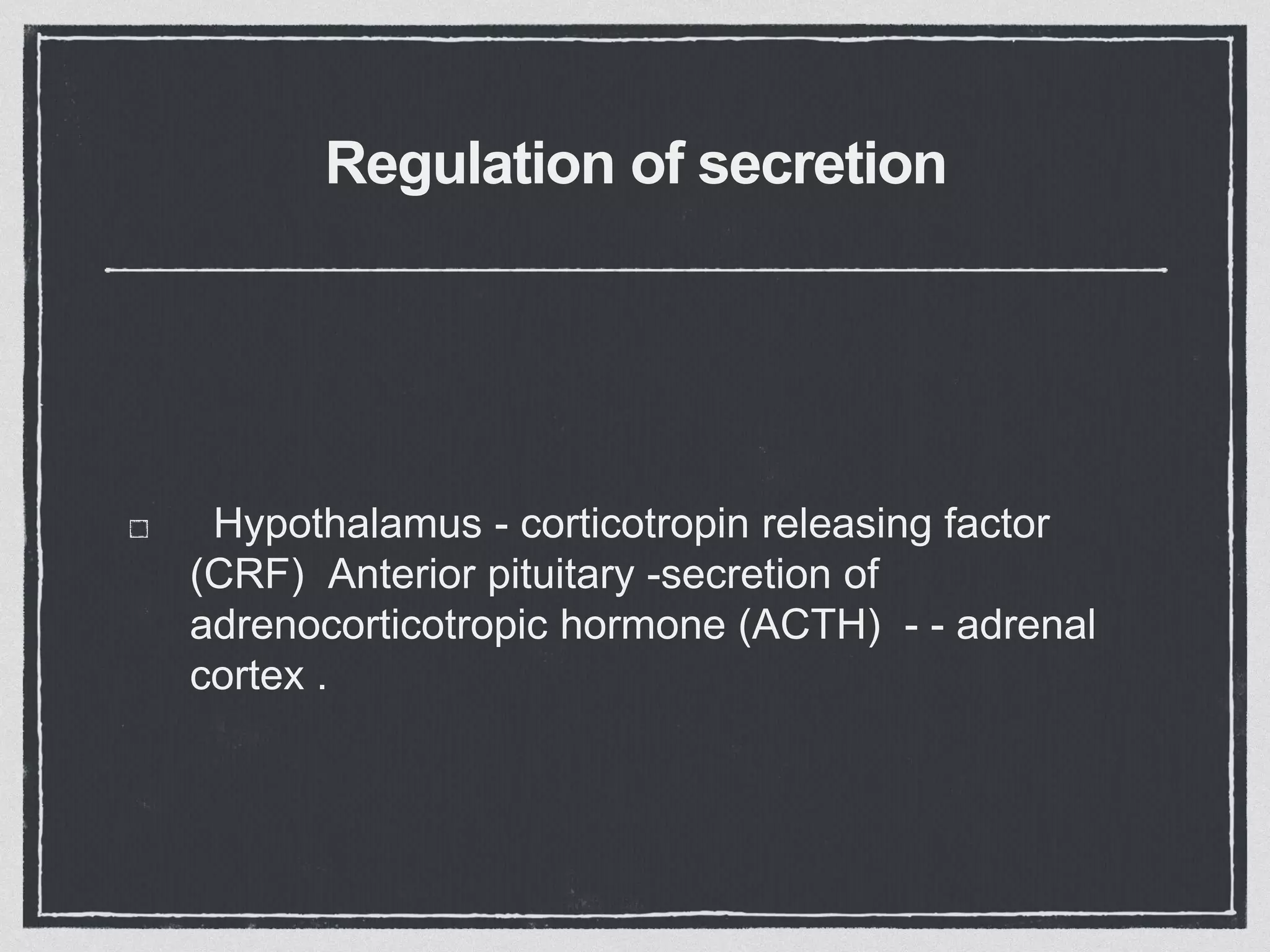
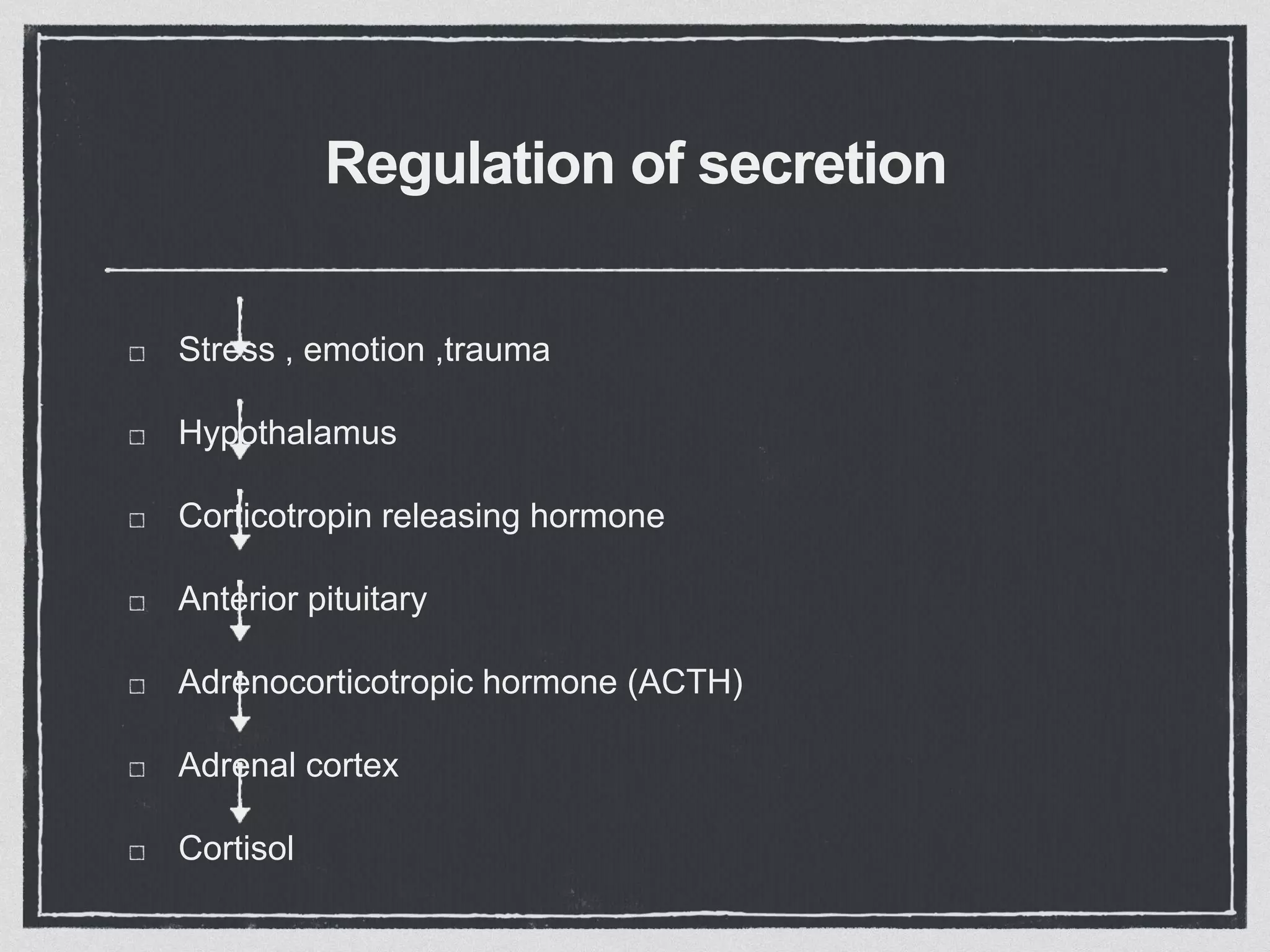
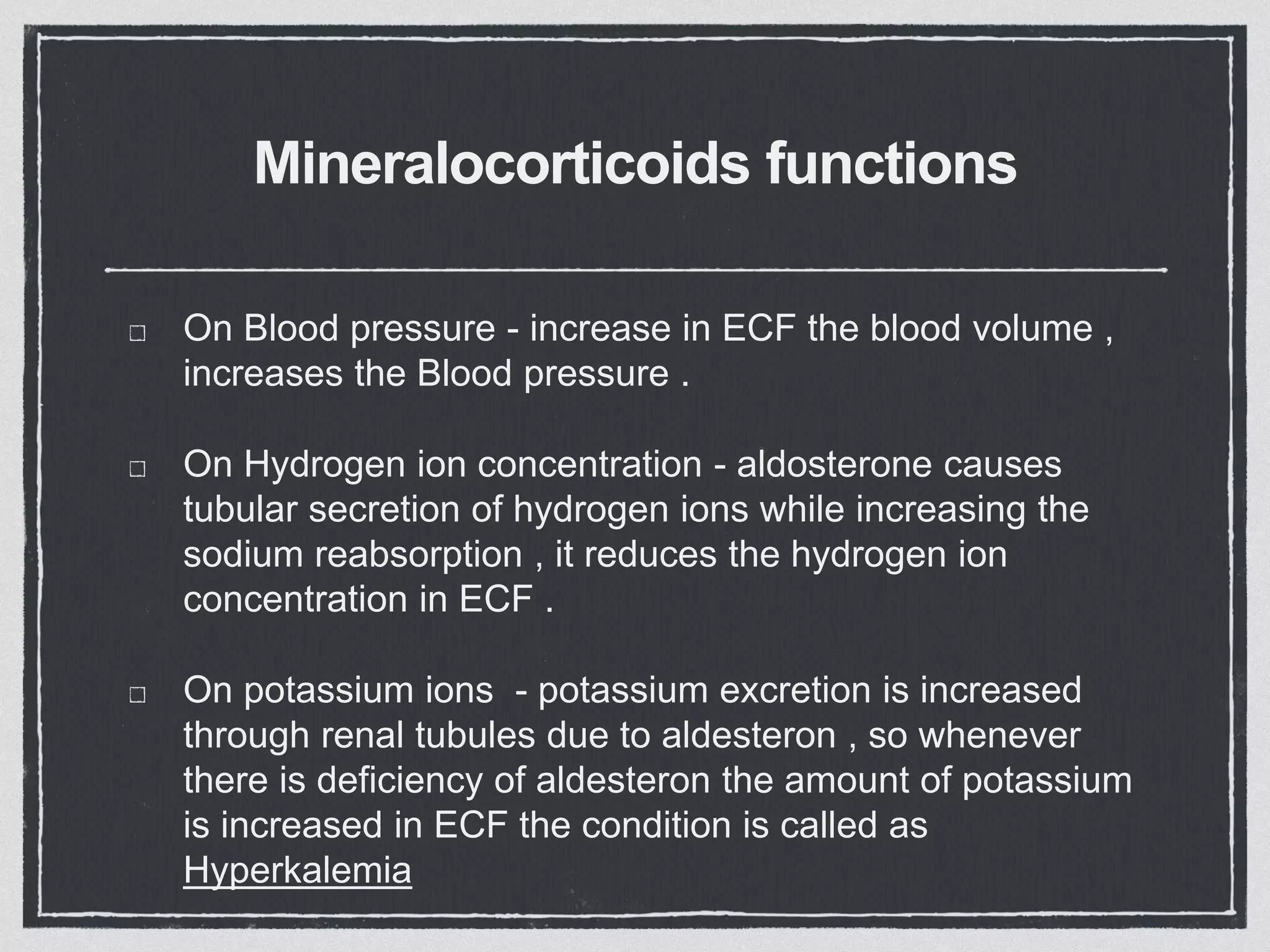
The adrenal cortex consists of three layers that secrete different hormones. The zona glomerulosa secretes mineralocorticoids like aldosterone that regulate sodium and potassium levels. The zona fasciculata secretes glucocorticoids like cortisol that regulate carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism and help the body respond to stress. The zona reticularis secretes small amounts of sex hormones. Diseases can result from too much or too little secretion of these hormones, causing symptoms like high blood pressure, muscle weakness, and changes in fat and sugar levels.