This document discusses various methods for valuing a corporate business, including:
1. The discounted cash flow method, which values a business based on its future free cash flows discounted at the firm's weighted average cost of capital.
2. Relative valuation methods like comparable company analysis and comparable transaction analysis, which derive valuation multiples from similar public companies or M&A transactions.
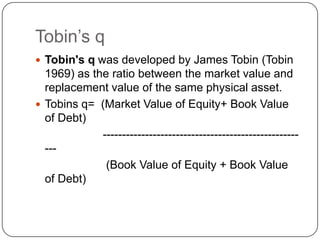
3. Other methods like the net asset value approach and Tobin's Q, which value a business based on its asset book values.
The document provides steps and considerations for each method to determine a company's economic worth based on its financials, industry, and investment characteristics.