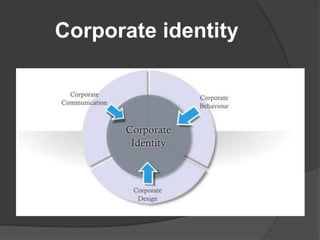
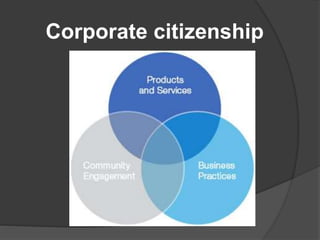
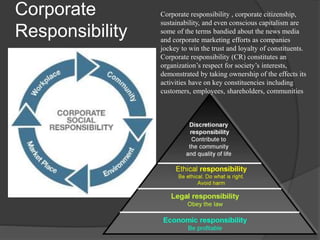
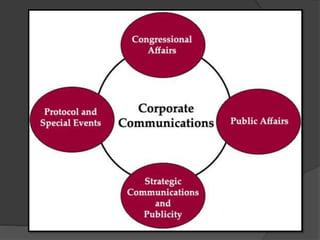
Corporate communication is a strategic tool that helps corporations gain competitive advantages and integrate diverse communication processes to define corporate image and improve performance. Key components include corporate branding, responsibility, reputation, crisis communications, and public relations, all aimed at fostering a strong culture and coherent identity. Effective corporate communication enhances stakeholder trust and manages challenges to an organization's reputation.