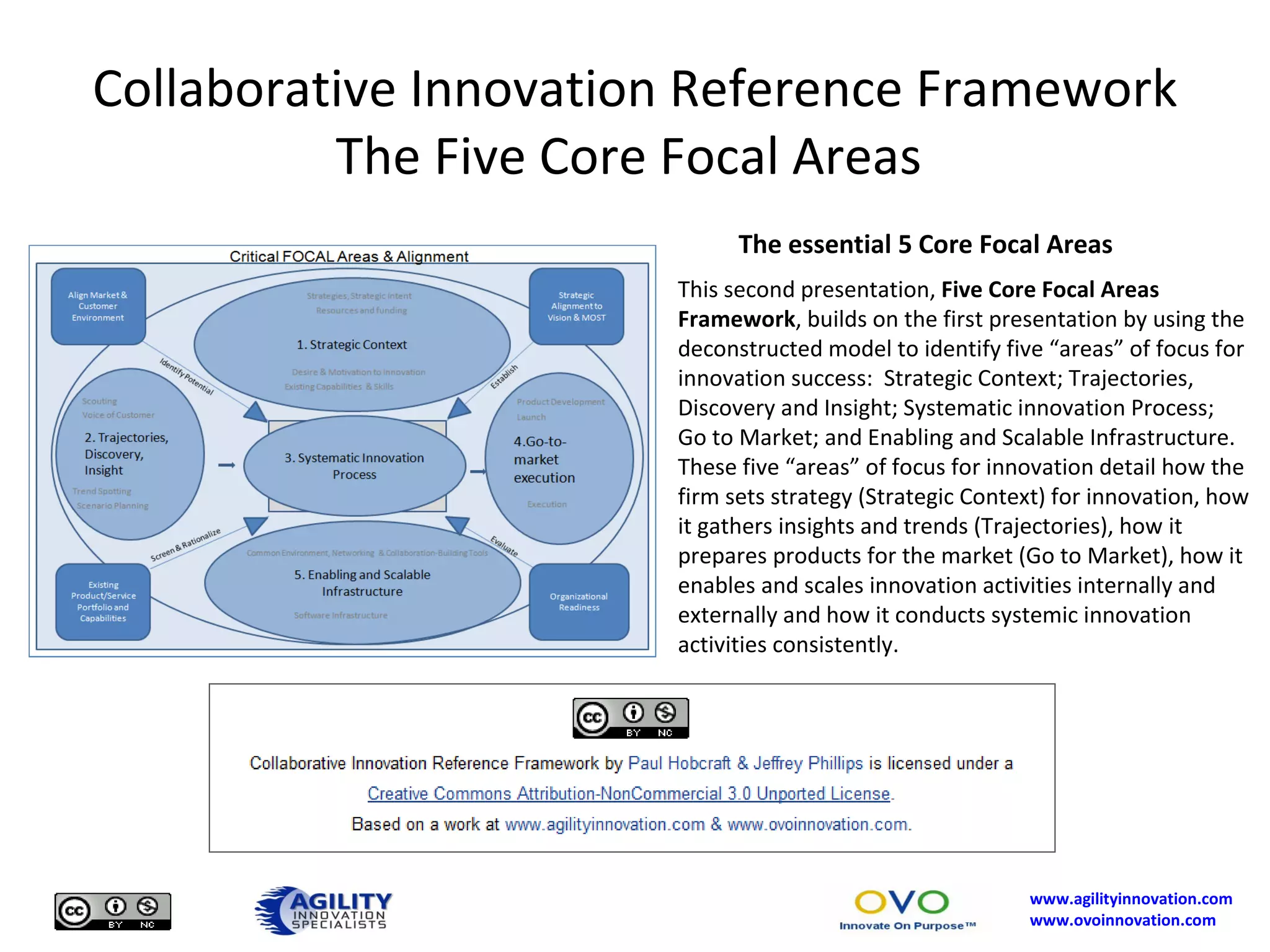
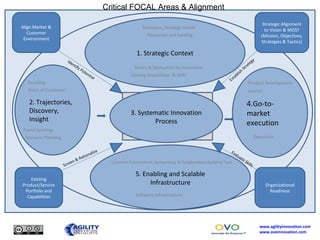
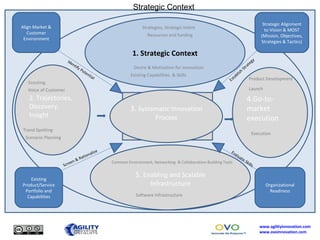
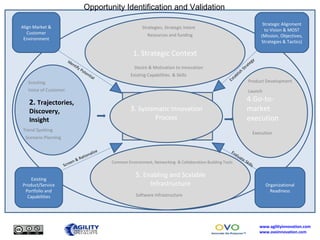
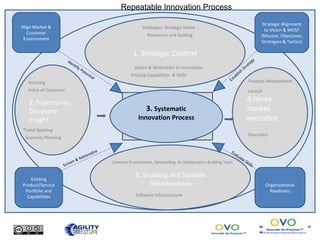
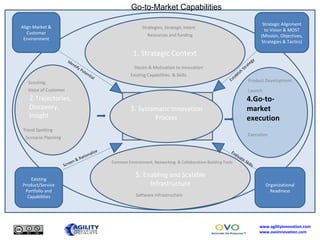
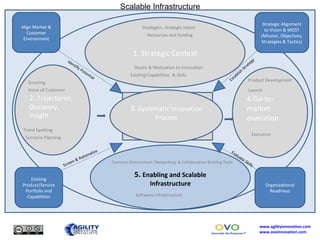
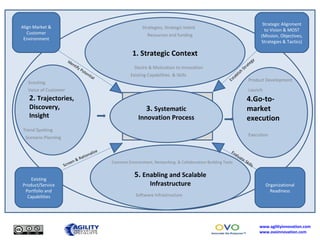
The document outlines a collaborative innovation reference framework focusing on five core areas essential for innovation success: strategic context, trajectories, systematic innovation process, go-to-market execution, and enabling infrastructure. It emphasizes the importance of aligning organizational strategies with customer insights, managing the innovation process systematically, and sustaining innovation efforts over time. The goal is to establish a common innovation model that simplifies understanding and fosters collaboration across various industries and markets.


















![Paul Hobcraft Email : [email_address] Phone Number +65 91 751 4350 Jeffrey Philips Email: [email_address] Phone Number +01 919-844-5644 Contact Details Collaborative Innovation Reference Framework For Europe, Africa, Middle East & Asia For North & South America Go to the Wiki on http://cirf.pbworks.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coreinnovationreferenceframework-110413121919-phpapp01/85/Core-innovation-reference-framework-28-320.jpg)