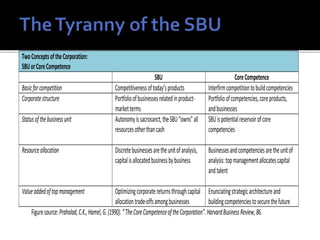
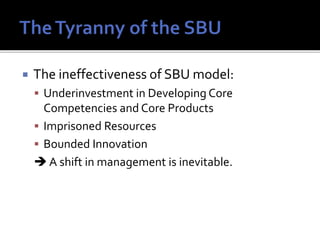
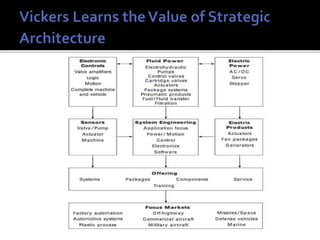
The document discusses the concept of core competencies as presented by Prahalad and Hamel. It defines core competencies as unique bundles of skills that are sources of competitive advantage. It argues companies should shift focus from managing business units to identifying, building, and leveraging core competencies across business units. This requires strategic architectures to guide competency development and consistency in allocating resources. Developing core competencies better positions companies for long-term leadership rather than short-term gains from individual business units.