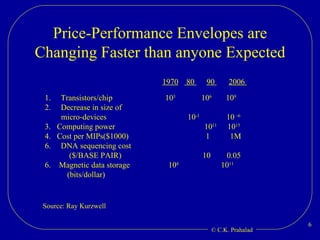
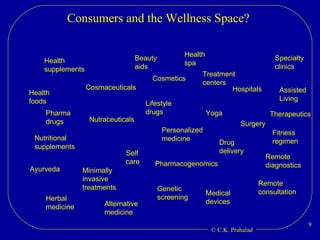
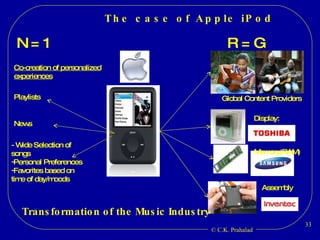
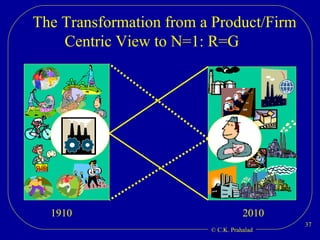
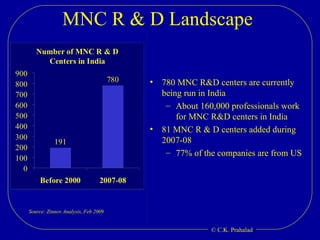
The document discusses the opportunities for entrepreneurship and innovation in India given various trends like globalization, connectivity, digitization, and the convergence of technologies. It argues that commercial value will be created at the intersection of multiple scientific disciplines to address challenges like aging, climate change, and chronic diseases. However, scientific discoveries are increasingly specialized and geographically distributed, creating a need for collaborative capacity to stitch together solutions. Entrepreneurship can help mobilize talent and resources globally to reduce the time and cost of moving science from the lab to the market. India has an opportunity to become a global source of innovations by leveraging its access to talent and collaborative capacity.