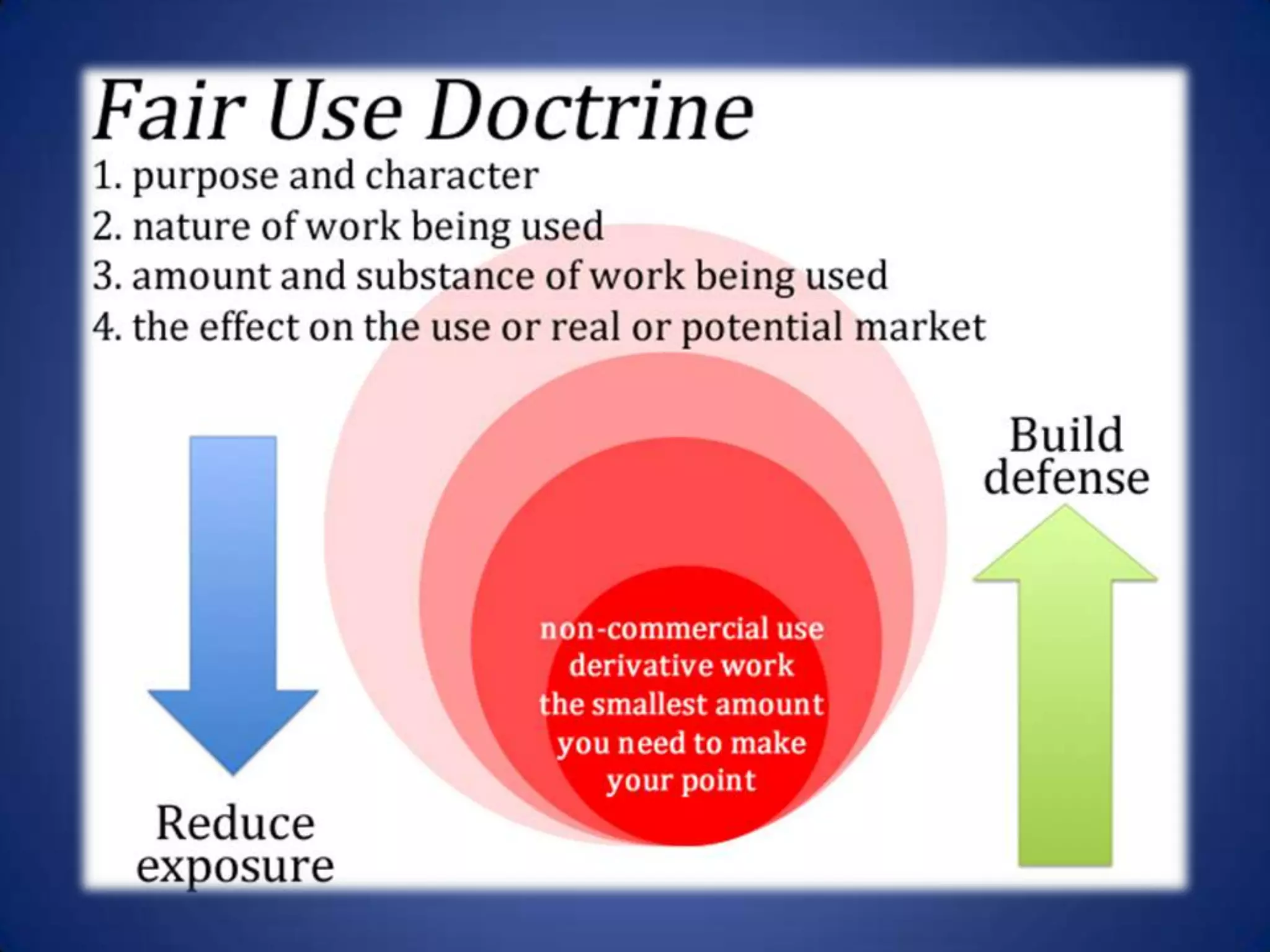
Copyright is a form of protection given to authors of original creative works under U.S. law. It is an automatic property right that can be sold or transferred and provides owners with exclusive rights over reproducing, distributing, publicly displaying, or making derivative works of the copyrighted work. Copyright law is outlined in Title 17 of the U.S. Code and the Copyright Act of 1976, and it provides certain exceptions for fair use, works in the public domain, library use, and some alternative licenses.