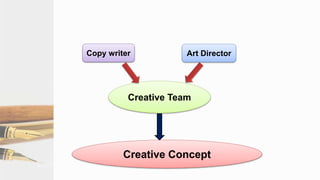
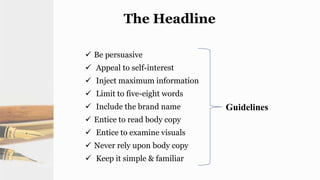
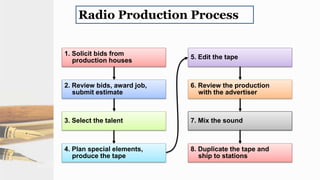
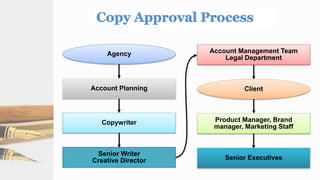
The document provides guidelines for copywriting across various media, including print, radio, television, and digital. It discusses the key elements of a creative plan and copywriting process. This includes developing headlines, subheads, and body copy for print ads. It also outlines formats and guidelines for writing effective radio, television, and online copy. The goal is to express a brand's value through written descriptions in a coherent manner tailored to the specific media channel.