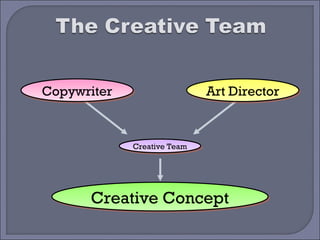
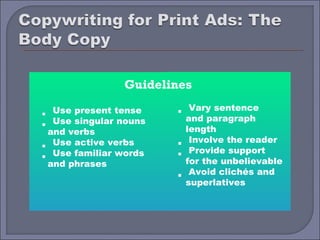
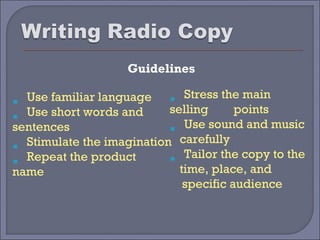
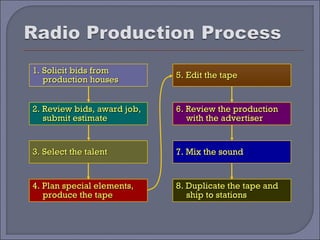
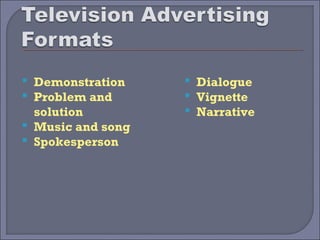
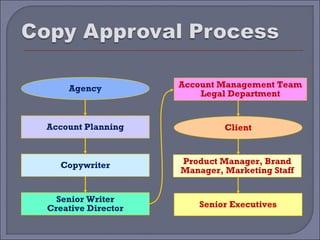
This document provides guidelines and best practices for different types of advertising copywriting and media, including print, radio, television, and slogans. It discusses the roles of copywriters and art directors in developing creative concepts and campaigns. It also provides examples and discusses techniques for writing effective headlines, body copy, subtitles, and guidelines for each media type.