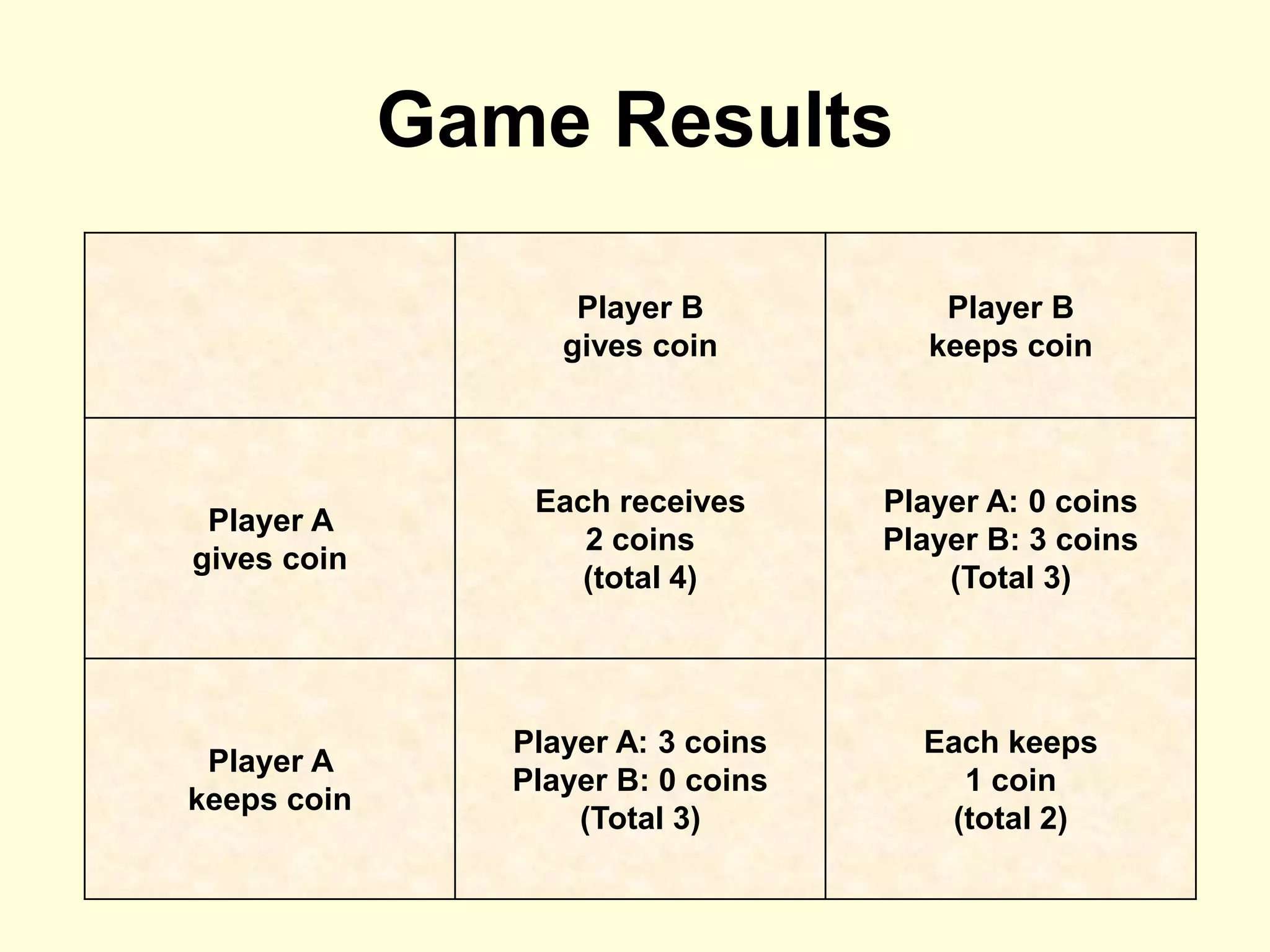
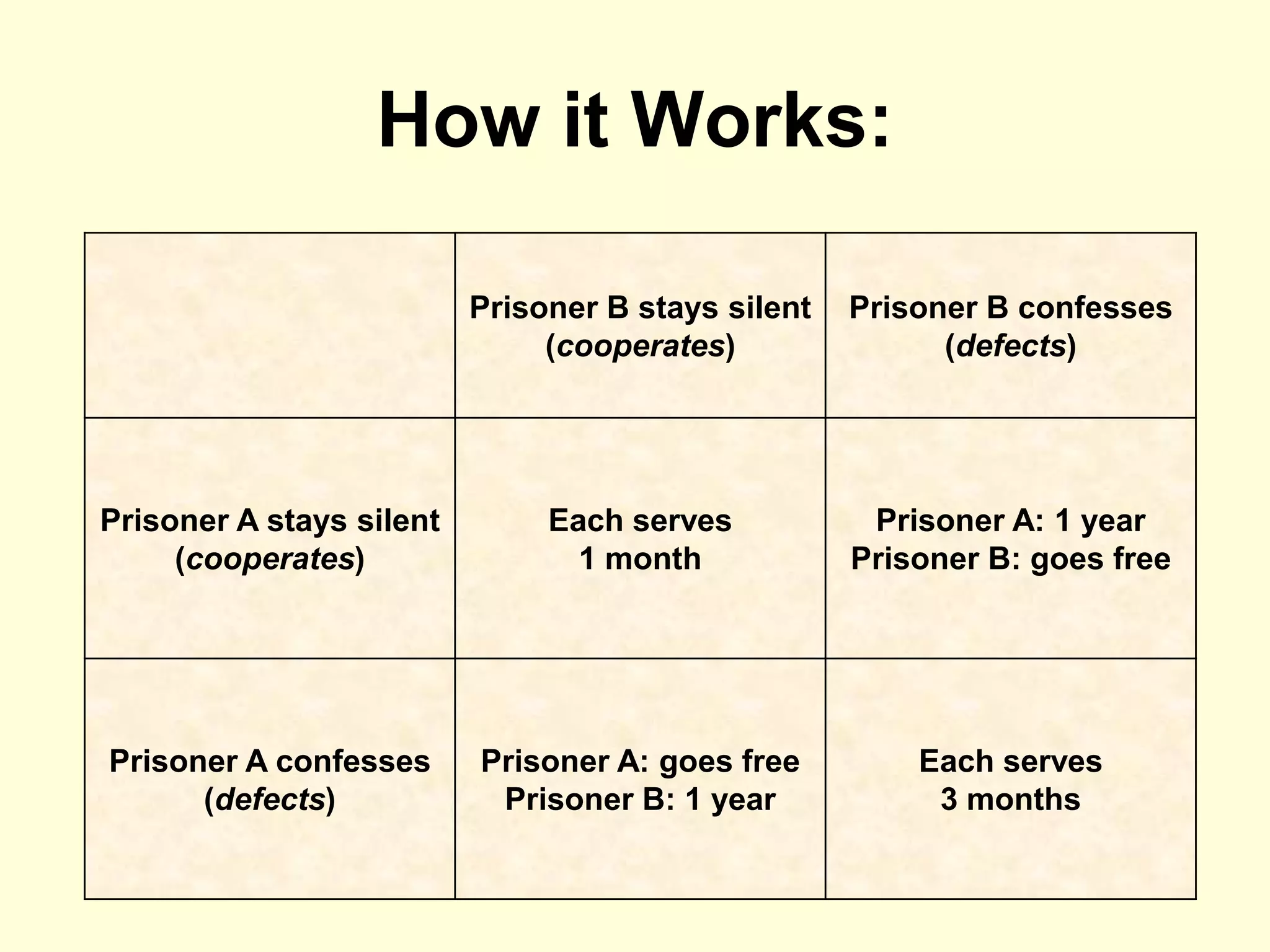
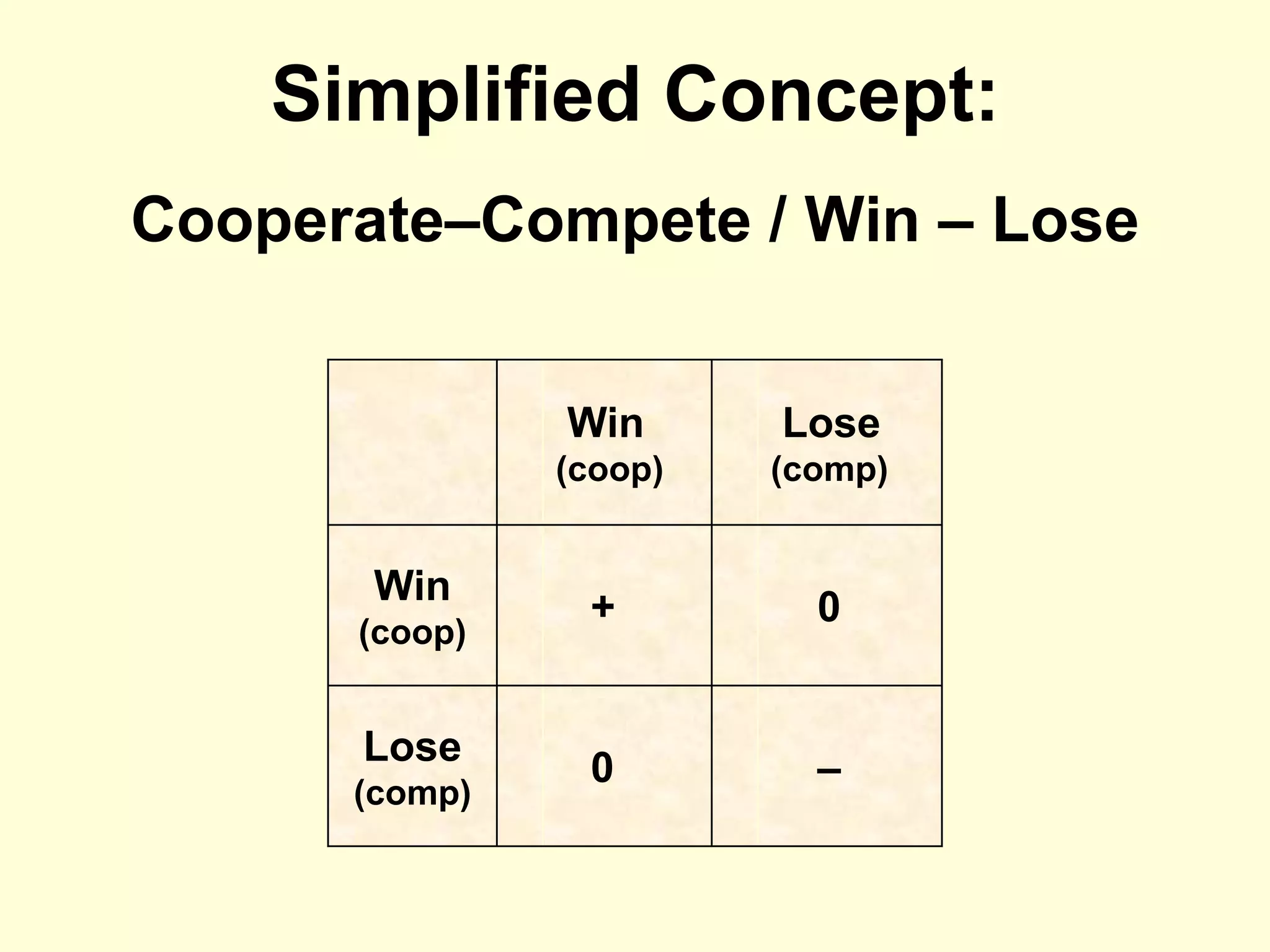
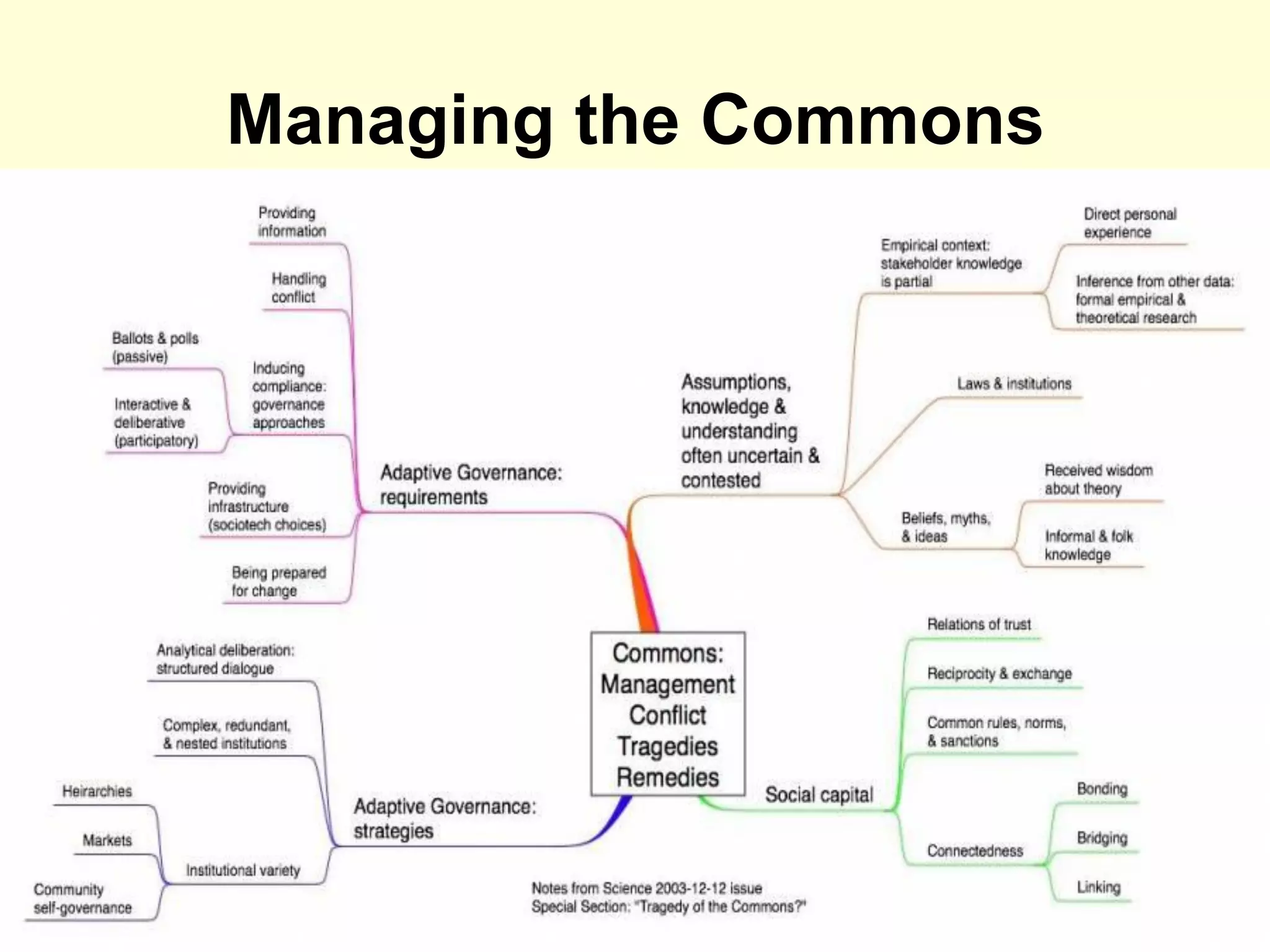
The document discusses cooperation theory through a series of examples, including the money game and the prisoner's dilemma, highlighting how self-interest can lead to collective irrationality and social dilemmas. It emphasizes the importance of cooperation over competition for social progress, supporting this with findings from historical and contemporary studies. The conclusion suggests a need for a formal theory of cooperation and multidisciplinary approaches to foster unity and sustainability.