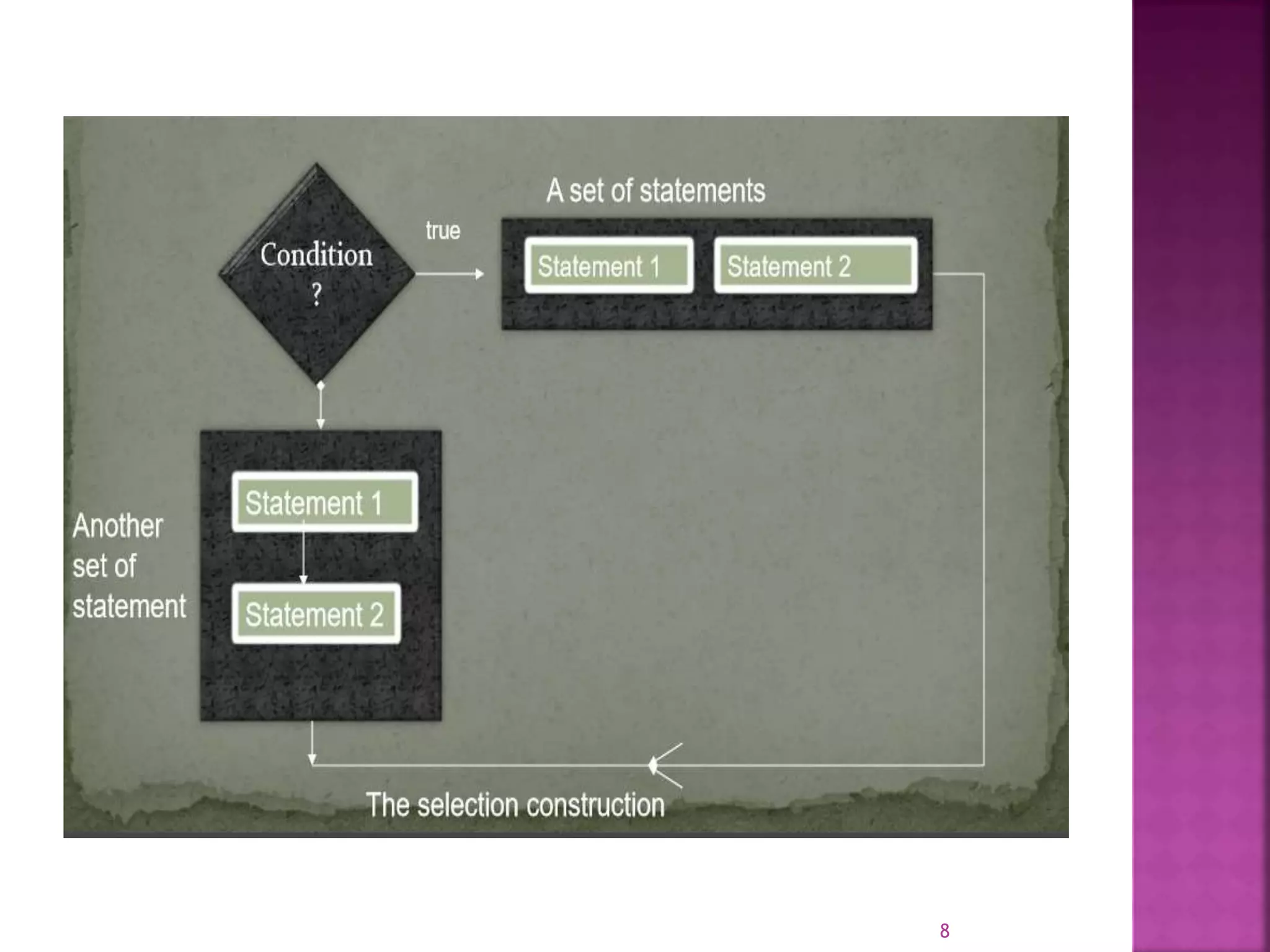
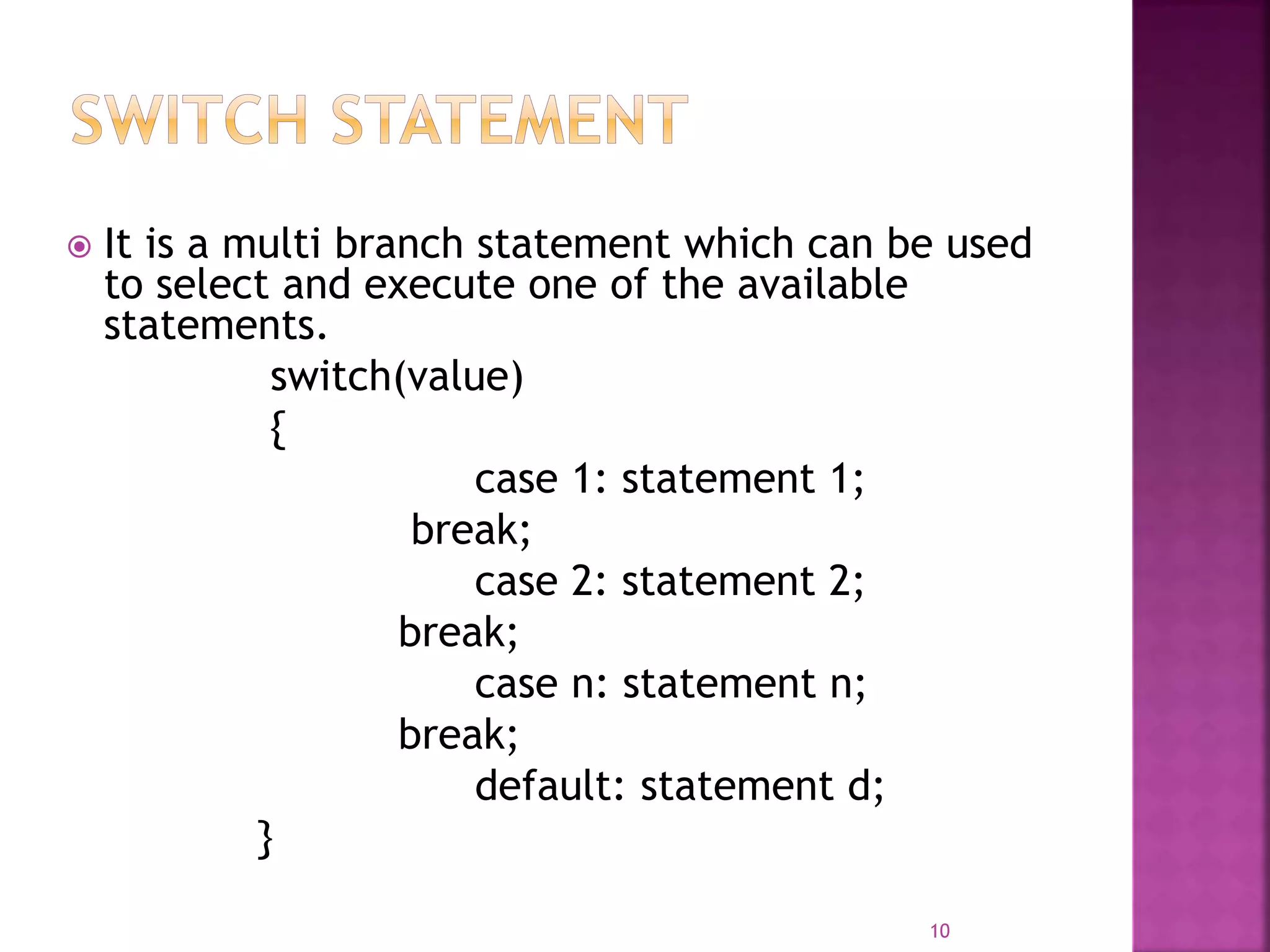
This document discusses different types of control flow statements in C++ including selection statements like if/else and switch statements, iteration statements like for, while, and do-while loops, and jump statements. Selection statements allow a program to choose one of several paths to execute based on conditions, while iteration statements repeat parts of a program. Jump statements abruptly transfer control from one part of a program to another. The document provides examples of how each type of statement is structured in C++ code.