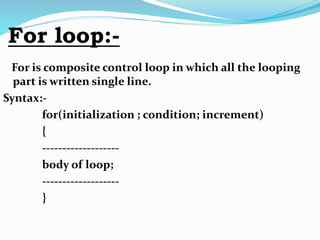
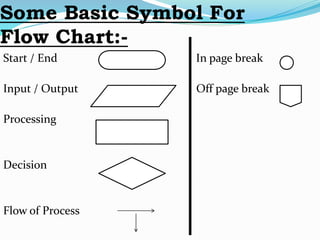
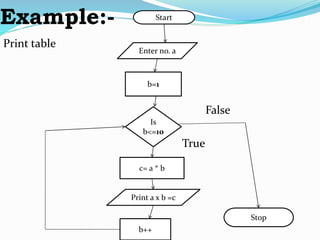
This document discusses looping statements and flow charts. It describes two types of looping statements: entry control loops like for and while that check the condition first before executing the code block, and exit control loops like do-while that execute the code block first before checking the condition. It provides examples of each loop type and explains the syntax. It also discusses flow charts, describing them as diagrams that show the order and relationship of operations to solve a problem, and lists some basic flow chart symbols.