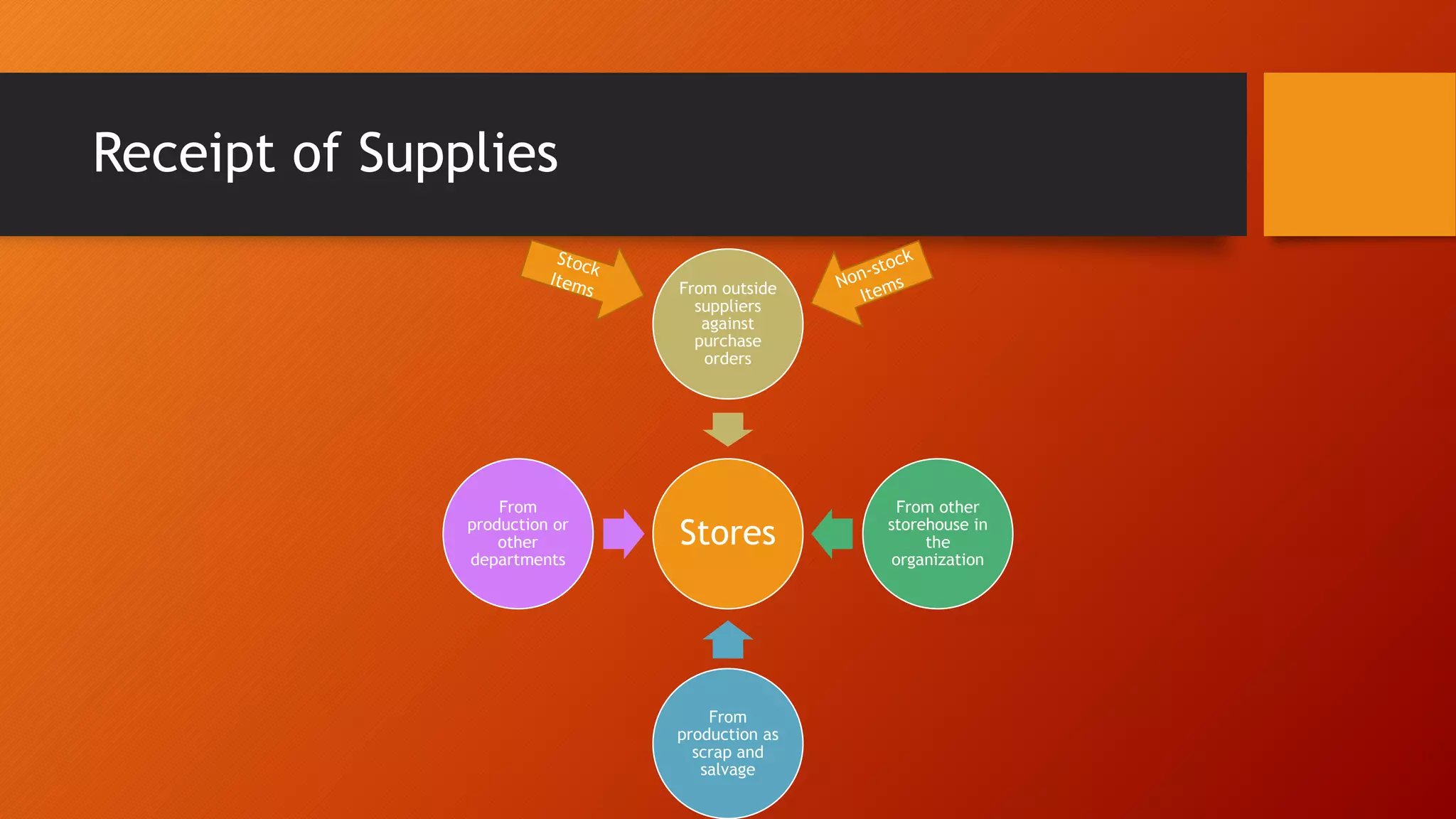
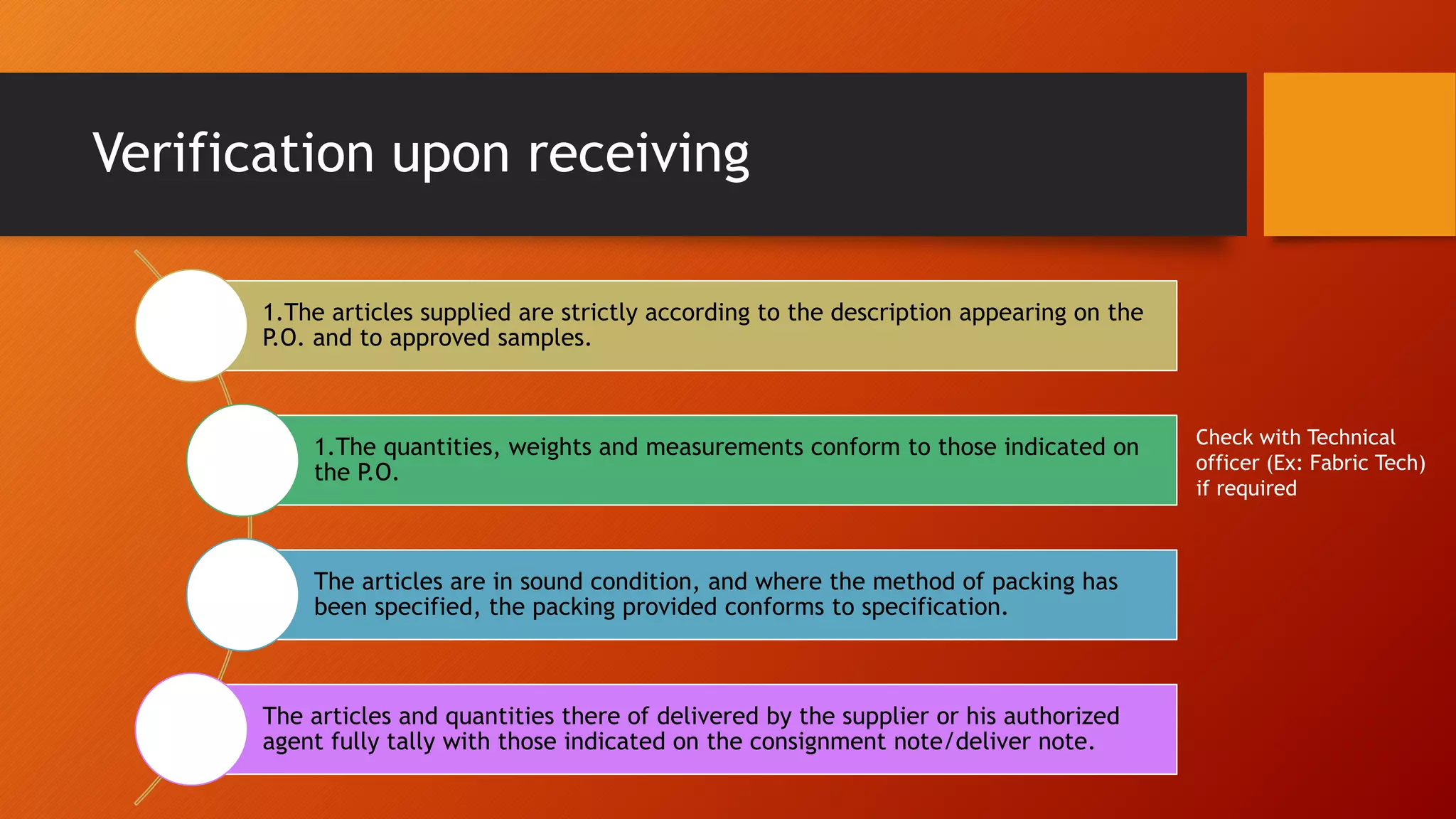
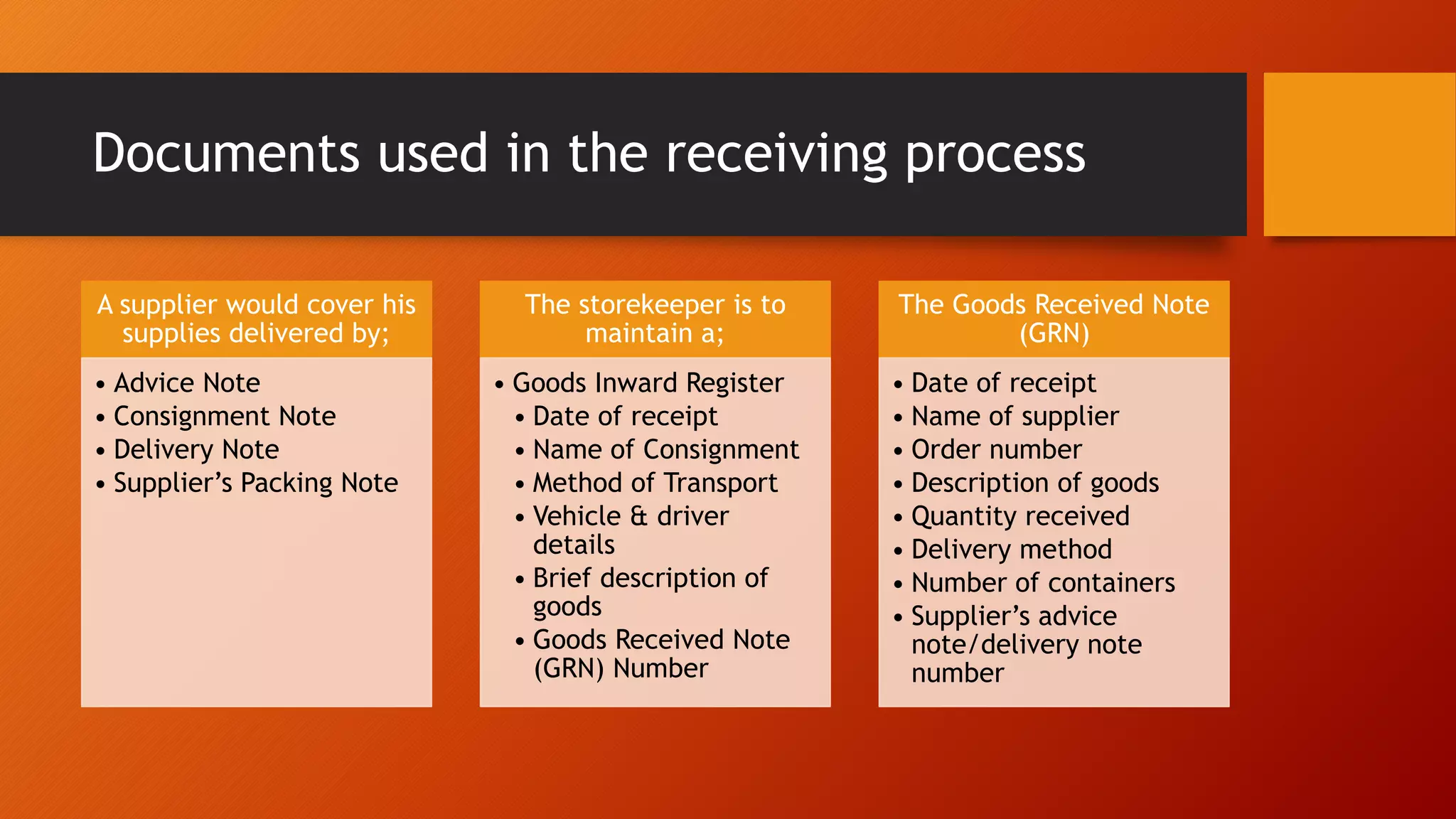
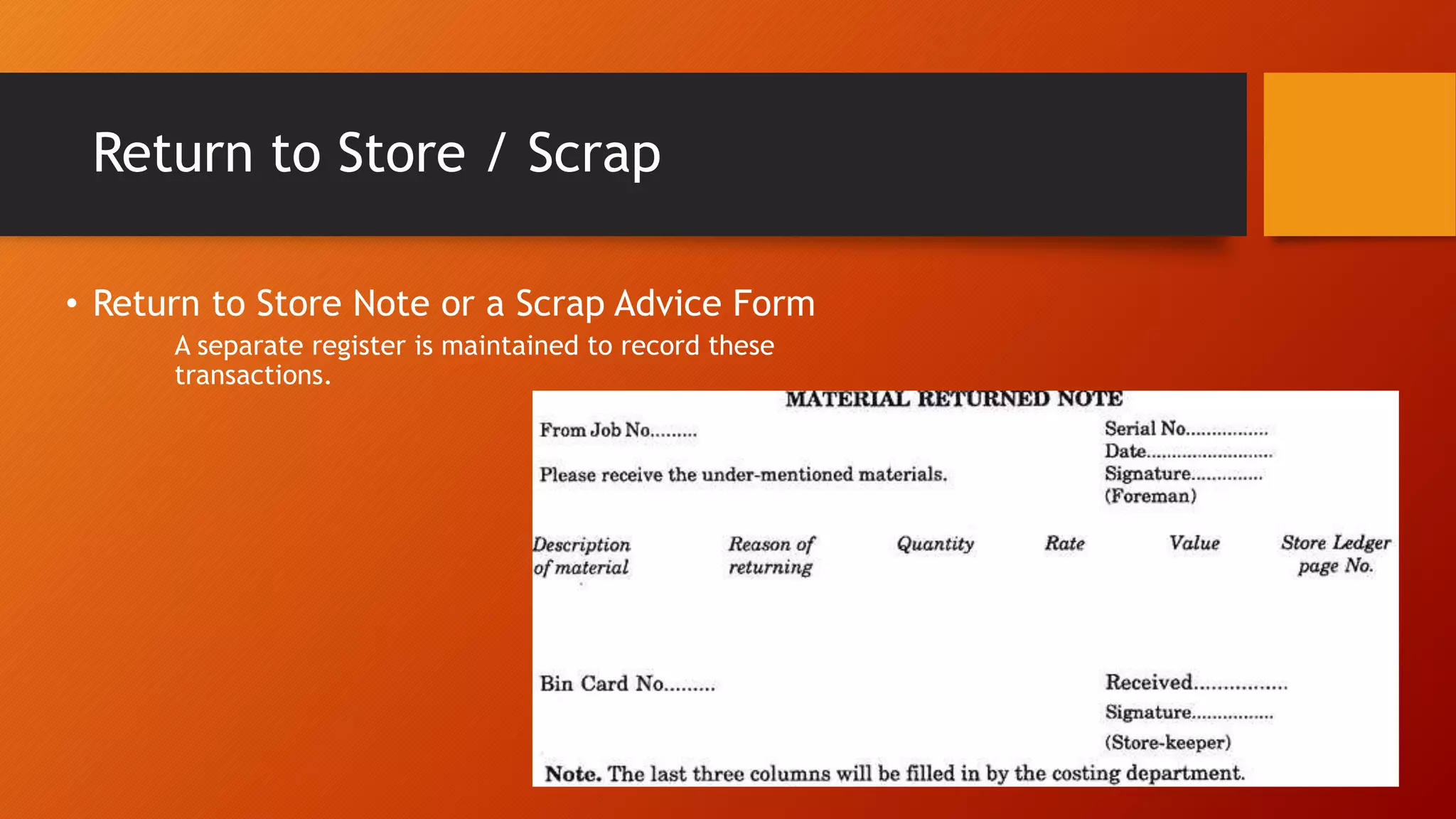
The document discusses control of receipts in a stores department. It defines a receipt as written acknowledgment of a transfer of value. Controlling the receiving process is important to prevent internal costs from failures. Receipts can come from outside suppliers, other storehouses, production as scrap or salvage, or other departments. Verification upon receiving includes checking quantities, condition, and packing against purchase orders. Partial or full rejection of supplies follows procedures. Documents used include advice notes, consignment notes, delivery notes, packing lists, goods inward registers, goods received notes, and transfer or scrap notes. Stores supervision aims to provide clear procedures and audits to reduce errors and fraud.