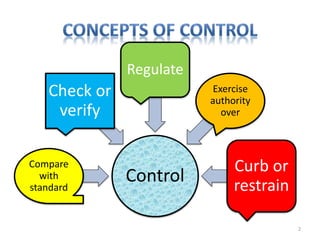
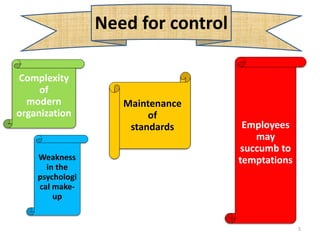
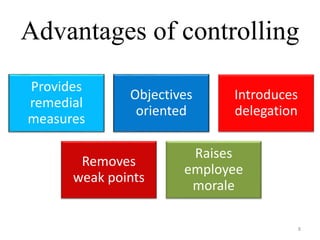
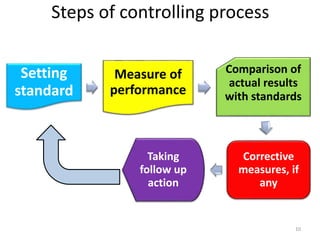
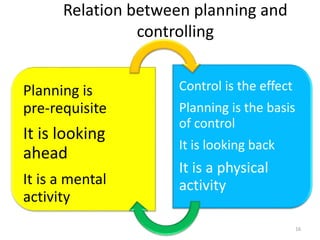
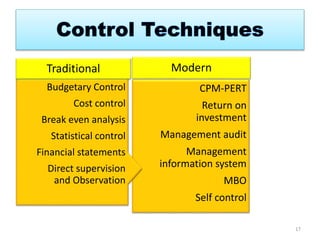
The document discusses the principles of control in management. It defines control as measuring and correcting performance to ensure objectives are achieved. Control involves setting standards, measuring performance, comparing results to standards, introducing corrective measures if needed, and following up. Traditional control techniques discussed include budgetary control, cost control, statistical control, and financial statements. Modern techniques mentioned are critical path method (CPM), program evaluation and review technique (PERT), return on investment, management audit, and management by objectives (MBO). The relationship between planning and control is also explained, with planning establishing the basis for control.