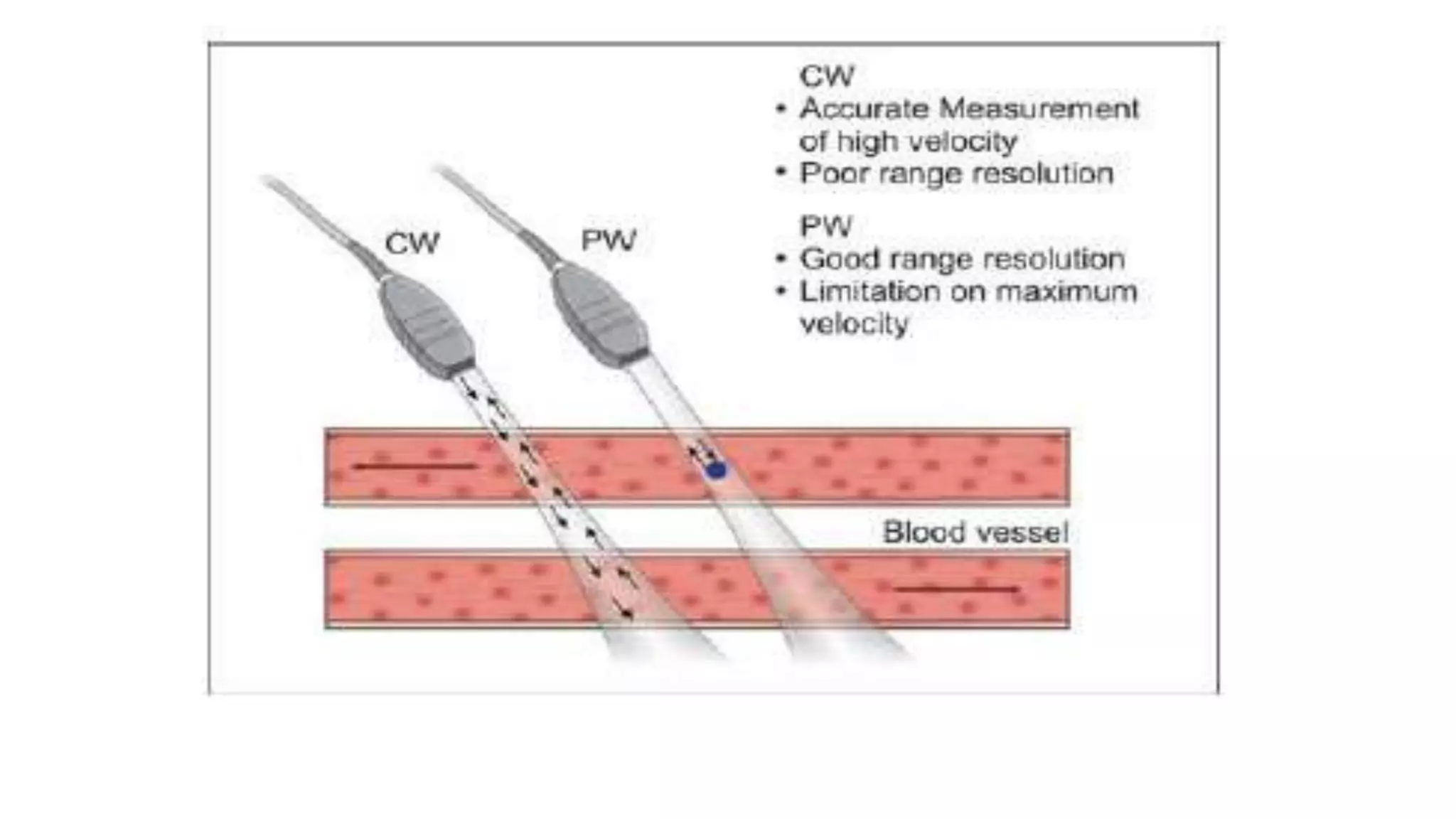
Continuous wave Doppler devices use two crystals where one constantly transmits ultrasound waves and the second receives signals reflected from red blood cells. They lack axial resolution since they measure reflected waves from the entire beam. Pulsed wave Doppler uses a single piezoelectric element that alternates transmitting and receiving ultrasound. It can precisely locate the source of frequency shifts in the axial direction and define the distance to a sample volume but is limited in the velocity of blood flow it can detect. Modern sonographers primarily use pulsed wave Doppler for its advantages over continuous wave.