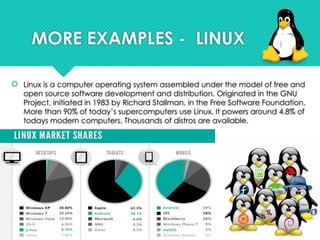
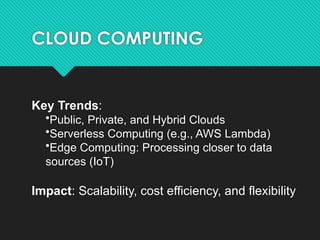
The document discusses contemporary software platform trends, highlighting key areas such as open source, network monitoring, cloud computing, microservices architecture, DevOps, artificial intelligence, low-code/no-code development, blockchain, and quantum computing. It explains the advantages and disadvantages of open source software, provides examples, and details on licenses and their implications. Additionally, it outlines the importance of cybersecurity, APIs, and integration in the modern software landscape.