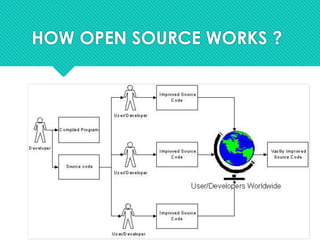
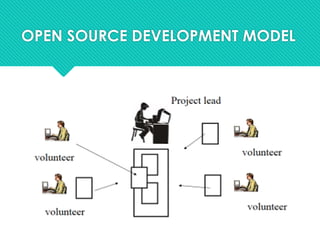
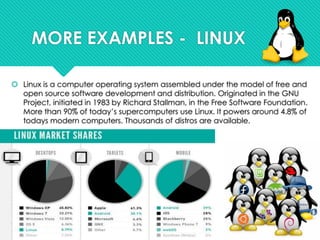
The document defines open source as a philosophy that promotes free redistribution and access to a product's design, ideas, and implementation details. Open source software is released to the development community for further evolution, whereas closed source software is developed privately by a small team. Open source has advantages like availability of source code, not depending on vendors, better quality/customizability, and lower costs compared to proprietary software. However, open source can also have disadvantages like a learning curve, incompatibility issues, and lack of financial incentives for developers. Popular examples of open source include Android, Linux, Firefox, and LibreOffice. The document also discusses open source licensing and common myths about open source software.