1) The document discusses consumer buying behavior and the factors that influence it. It defines key terms like consumer, customer, and consumer market.
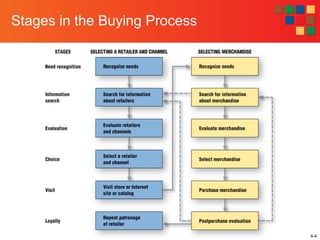
2) It outlines the stages in the buying process - need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase evaluation.
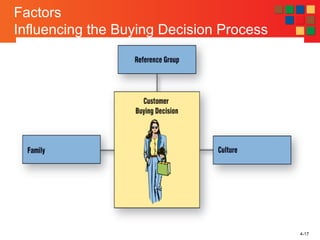
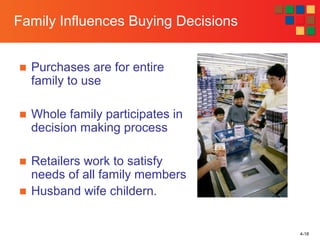
3) The factors that influence buying decisions are discussed - cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors like reference groups, family, culture, social class, age, and personality.