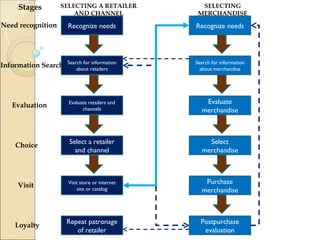
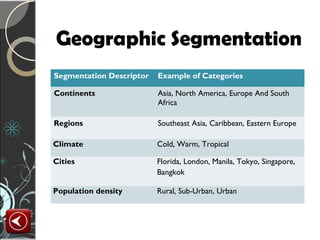
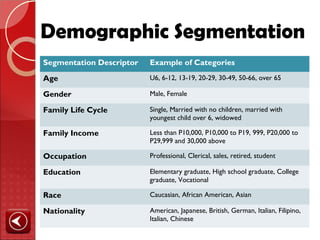
This document summarizes the key stages in a consumer's buying process including need recognition, information search, evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. It discusses factors that influence the buying process like the type of need, characteristics of the consumer, and the buying situation. The types of buying decisions are also outlined as being extended problem solving, limited problem solving, or habitual decision making. Social influences on the buying process from family, reference groups, and culture are highlighted. Finally, the document summarizes different approaches to segmenting markets including geographic, demographic, geodemographic, lifestyle, usage situation, and benefit segmentation.