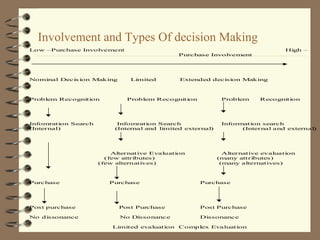
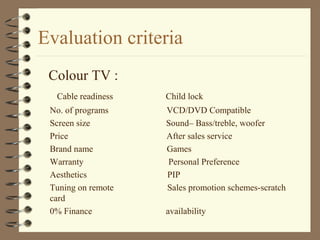
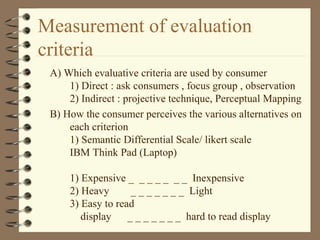
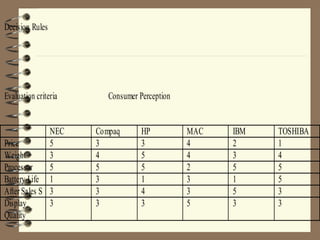
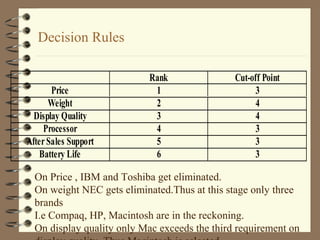
The document discusses the consumer buying decision process, including problem recognition, information search, alternative evaluation and selection, and post-purchase behavior. It also covers types of consumer decisions based on purchase involvement (habitual, limited, extended decision making) and the different levels of information search that correspond. Marketing strategies are proposed based on the decision making process and type, such as maintenance strategies for habitual purchases or intercept strategies for brands not in a consumer's evoked set during limited decision making. Evaluation criteria are provided for various product categories like color TVs, shaving cream, cameras, and automobiles.