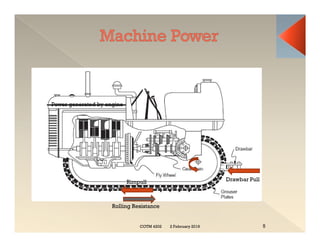
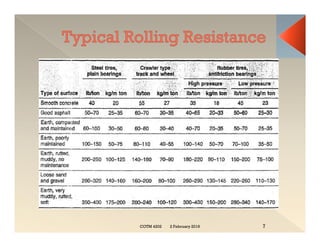
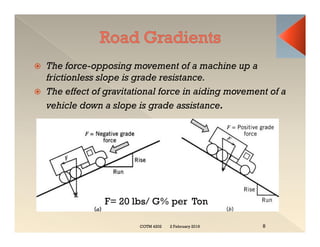
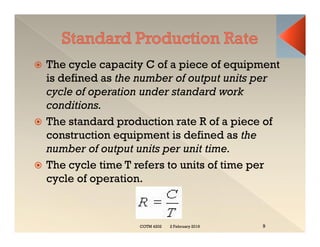
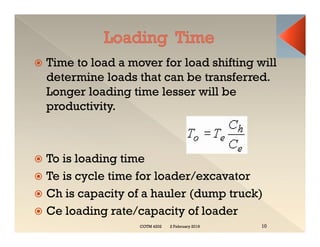
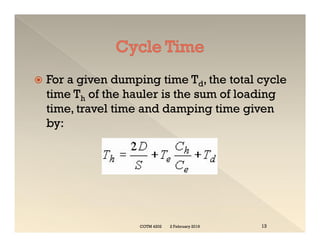
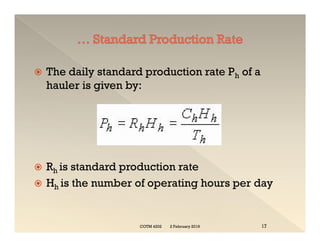
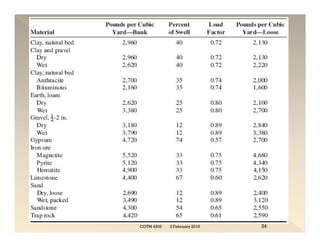
This document discusses concepts related to construction equipment and plant management. It defines key terms like estimating, equipment selection, cycle time, production rate, hauling parameters, and material properties. Equations are provided to calculate cycle time, optimum number of haul units, daily production rates, and material volumes under different conditions. Factors that influence hauling productivity like loading time, travel time, and delays are also examined.