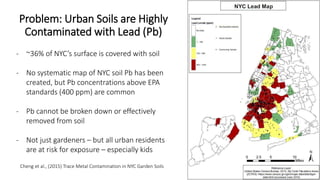
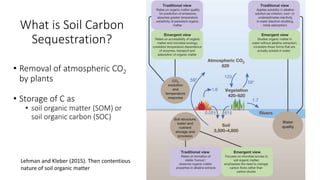
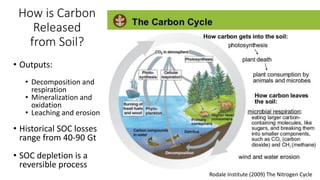
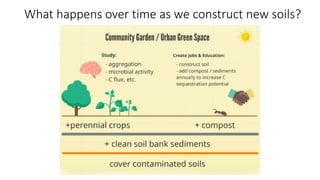
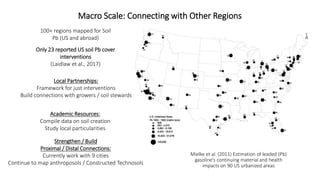
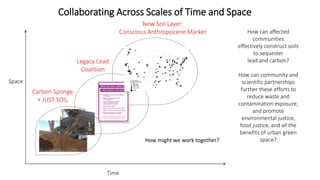
The presentation discusses the high levels of lead contamination in urban soils, particularly in NYC, and explores potential solutions for remediation and carbon sequestration. It highlights the creation of the NYC Clean Soil Bank, which provides safe soil mixtures for community gardening and emphasizes the importance of community partnerships in addressing soil contamination and promoting environmental justice. Key concepts include soil carbon sequestration processes and the use of compost to improve soil health while minimizing exposure risks.