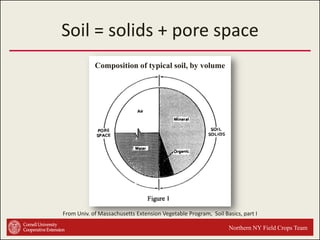
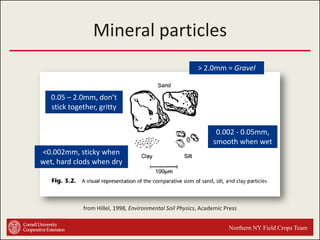
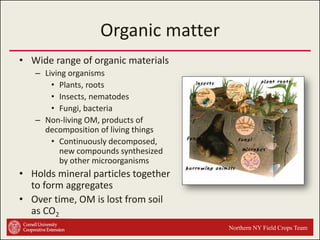
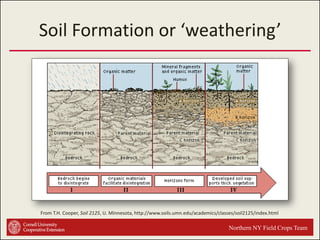
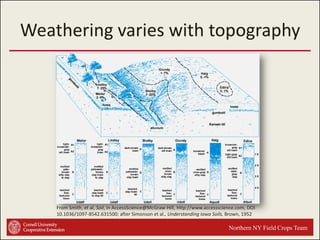
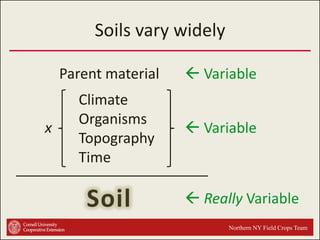
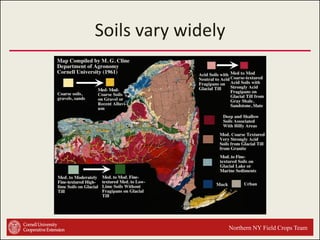
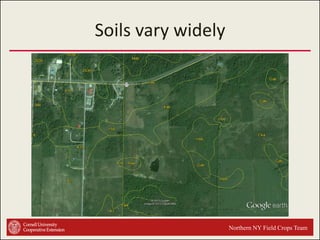
This document provides an introduction to soils. It explains that soil is formed over long periods of time through the weathering of parent materials influenced by climate, organisms, topography, and time. Soil is made up of minerals, organic matter, air, and water. It varies widely in different locations due to differences in these forming factors. Soil serves important functions such as growing plants, regulating water and nutrients, and providing habitat. Understanding soils is essential because nearly all life on earth depends on the various functions soils provide.